Large language models in business innovation are rapidly transforming how companies operate, compete, and innovate. This isn’t just about automating tasks; it’s about unlocking entirely new possibilities. Imagine AI-powered insights driving strategic decisions, personalized customer experiences exceeding expectations, and product development cycles accelerating at warp speed. This exploration dives deep into the real-world applications, potential pitfalls, and future trajectory of LLMs in the business world – from streamlining operations to sparking groundbreaking new ventures.
We’ll dissect how LLMs are currently being used across diverse sectors, from finance to marketing, highlighting both the impressive benefits and the inevitable challenges. We’ll examine the ethical considerations, explore the potential for disruption, and showcase successful real-world examples of companies leveraging LLMs for a competitive edge. Get ready to see how this technology is not just shaping the future of business – it’s actively building it.
Business Applications of Large Language Models
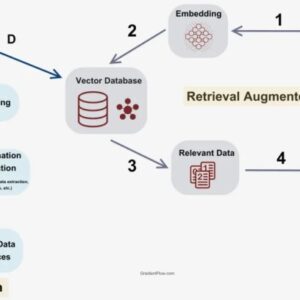
Source: 9series.com
Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly transforming the business landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for increased efficiency, improved customer experiences, and the development of entirely new products and services. Their ability to understand and generate human-like text opens doors to applications previously confined to the realm of science fiction. This section explores the practical applications of LLMs across various sectors and their impact on the modern workplace.
LLM Applications Across Business Sectors
The versatility of LLMs is evident in their adoption across diverse sectors. Their capabilities are being harnessed to streamline operations, enhance customer interactions, and drive innovation. The following table provides a snapshot of current applications and their associated benefits and challenges.
| Sector | Application | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finance | Fraud detection, risk assessment, financial report summarization, chatbot for customer support | Reduced operational costs, improved accuracy, faster decision-making, enhanced customer service | Data privacy concerns, model bias, need for robust validation and auditing |
| Marketing | Content creation (blog posts, ad copy), personalized email marketing, social media management, market research analysis | Increased efficiency in content production, improved targeting and personalization, better understanding of customer preferences | Maintaining brand voice consistency, ensuring ethical and responsible use of AI-generated content, managing potential for misinformation |
| Customer Service | Chatbots for instant support, automated email responses, sentiment analysis of customer feedback | Improved customer satisfaction, reduced response times, 24/7 availability, cost savings | Handling complex or nuanced customer inquiries, ensuring seamless human handoff when needed, managing customer expectations |
| Healthcare | Medical report summarization, drug discovery, patient support chatbots, personalized treatment recommendations | Improved efficiency in administrative tasks, accelerated research and development, enhanced patient care | Data security and privacy concerns, regulatory compliance, ensuring accuracy and reliability of medical information |
Automating Repetitive Tasks and Empowering Human Employees
LLMs excel at automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human employees to focus on higher-level strategic initiatives. For example, in legal firms, LLMs can automate contract review, identifying key clauses and potential risks, allowing lawyers to concentrate on legal strategy and client interaction. Similarly, in customer service, LLMs can handle routine inquiries, leaving human agents to address more complex and sensitive issues requiring empathy and nuanced understanding. This shift allows for a more efficient and fulfilling work environment, fostering creativity and innovation. The result is a workforce that is more engaged and productive.
Improving Customer Experience Through Personalized Interactions
LLMs significantly enhance customer experience by enabling personalized interactions and efficient support. By analyzing customer data, LLMs can tailor communications, product recommendations, and support responses to individual preferences and needs. This personalized approach fosters stronger customer relationships and boosts loyalty. For instance, an e-commerce platform can use an LLM to recommend products based on a customer’s browsing history and past purchases, creating a more engaging and relevant shopping experience. Furthermore, LLMs can provide instant and accurate answers to customer inquiries through chatbots, improving response times and overall satisfaction. This leads to increased customer retention and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
LLMs and Enhanced Decision-Making
Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing how businesses approach decision-making. Their ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data, far exceeding human capabilities, unlocks previously unseen insights and patterns, leading to more informed and strategic choices. This shift towards data-driven decision-making, empowered by LLMs, is transforming various industries, from finance and marketing to healthcare and manufacturing.
LLMs analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns that inform better business decisions by leveraging advanced statistical methods and machine learning algorithms. Unlike traditional methods that often rely on smaller, more curated datasets and simpler analytical techniques, LLMs can handle the complexity and scale of big data, uncovering subtle correlations and predictive patterns that might otherwise remain hidden. This enhanced analytical power allows businesses to anticipate market shifts, optimize operations, and mitigate risks more effectively.
LLM Analysis Compared to Traditional Business Analytics
Traditional business analytics methods, while valuable, often face limitations in processing the sheer volume and variety of data now available. Methods like regression analysis or simpler statistical modeling might struggle with unstructured data (e.g., text from customer reviews or social media) or the complexity of interconnected variables within massive datasets. LLMs, however, can handle both structured and unstructured data, employing techniques like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to identify patterns and predict outcomes with greater accuracy and speed. For instance, while traditional methods might analyze sales figures to identify seasonal trends, an LLM could incorporate customer sentiment data from social media to predict future sales with greater precision, anticipating potential shifts in consumer preferences. This integration of diverse data sources offers a more holistic and nuanced understanding of the business landscape.
Hypothetical Scenario: Improving Inventory Management
Imagine a large retail chain struggling with inefficient inventory management. Traditional methods rely on forecasting models based on historical sales data and expert estimations. However, these models often fail to account for unforeseen events, such as sudden changes in consumer demand or supply chain disruptions. An LLM could significantly improve this process. By integrating sales data, weather patterns (affecting seasonal demand), social media trends (identifying popular products), and even news articles about competitor actions, the LLM can build a far more robust predictive model. This model would not only forecast demand more accurately but also identify potential risks and suggest proactive adjustments to inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and reducing storage costs. For example, if the LLM detects a surge in online searches for a particular product coupled with a news story about a competitor’s product recall, it could proactively increase the inventory of the substitute product, capitalizing on the increased demand and minimizing potential losses. This proactive, data-driven approach, powered by the LLM, leads to optimized inventory levels, reduced waste, and improved profitability.
Innovation through LLM-Powered Product Development: Large Language Models In Business Innovation
Large Language Models (LLMs) are no longer just a futuristic fantasy; they’re actively reshaping how businesses conceive, design, and launch products. Their ability to process and generate human-quality text unlocks unprecedented opportunities for innovation across the entire product development lifecycle. From initial brainstorming sessions to final marketing copy, LLMs are proving to be invaluable partners in the quest for market-leading products.
LLMs drastically accelerate the product development process by automating tedious tasks and providing insights that were previously inaccessible. This allows businesses to focus on what truly matters: creating innovative solutions that meet customer needs and drive growth. This isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about unlocking entirely new avenues of creativity and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Examples of LLM-Assisted Product Development
Several companies are already leveraging LLMs to create innovative products and services. For instance, Jasper, an AI-powered content creation platform, uses LLMs to help businesses generate marketing materials, website copy, and other content, effectively becoming a product itself, born from LLM technology. Other examples include the use of LLMs in developing personalized learning platforms, which adapt to individual student needs based on their writing style and progress, providing customized feedback and tailored learning paths. In the realm of software development, LLMs are assisting in code generation, testing, and documentation, significantly speeding up the development cycle and reducing the risk of errors. These are just a few examples of the transformative impact LLMs are having on product development.
LLMs Facilitate Brainstorming and Idea Generation
The initial brainstorming phase is crucial in product development. LLMs can significantly enhance this process by providing fresh perspectives and generating a wide range of ideas based on user prompts. For example, an LLM could be prompted with a problem statement like “Develop innovative solutions to improve the efficiency of online grocery shopping,” and it would generate numerous ideas, ranging from improved search functionality and personalized recommendations to innovative delivery methods and interactive shopping experiences. This broadens the scope of brainstorming beyond the limitations of human thinking, leading to more creative and comprehensive solutions. The LLM can also analyze market trends and competitor offerings, providing valuable context for idea generation. This ensures that the generated ideas are not only innovative but also commercially viable.
Integrating LLMs into a Product Development Workflow
Integrating LLMs into a product development workflow can be achieved through a structured, step-by-step process.
- Define the problem or opportunity: Clearly articulate the specific challenge or opportunity the new product aims to address.
- Gather relevant data: Collect market research, customer feedback, and competitor analysis to provide context for the LLM.
- Develop LLM prompts: Craft clear, concise, and targeted prompts to guide the LLM in generating relevant ideas and solutions.
- Generate and evaluate ideas: Use the LLM to generate a diverse range of ideas. Critically evaluate these ideas based on feasibility, market potential, and alignment with business goals.
- Refine and iterate: Use feedback from the evaluation phase to refine the ideas and iterate on the design.
- Develop prototypes: Create prototypes based on the refined ideas and test them with target users.
- Launch and iterate: Launch the product and continue to collect feedback to further refine and improve it based on real-world usage.
This structured approach ensures that the LLM is used effectively and efficiently throughout the product development process, maximizing its potential to drive innovation.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) in business presents exciting opportunities, but also raises significant ethical and practical challenges. Ignoring these risks could lead to reputational damage, legal issues, and ultimately, hinder the successful integration of LLMs into business operations. Responsible implementation requires a proactive approach to mitigating potential downsides and prioritizing ethical considerations.
Bias and Fairness in LLM Outputs
LLMs are trained on massive datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases (gender, racial, socioeconomic, etc.), the LLM will inevitably perpetuate and even amplify those biases in its outputs. This can manifest in discriminatory hiring practices, skewed product recommendations, or unfair loan applications, all with potentially devastating consequences. For example, an LLM trained on a dataset primarily featuring male voices might generate text that subtly reinforces gender stereotypes in marketing campaigns. Mitigating this requires careful curation of training data, ongoing bias detection and mitigation techniques, and human oversight in reviewing and validating LLM outputs, especially in high-stakes decision-making processes.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
LLMs often require access to sensitive business data and customer information to function effectively. This raises significant privacy and security concerns, particularly regarding data breaches and unauthorized access. Companies must implement robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques, to protect sensitive information. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations (like GDPR and CCPA) is paramount. A breach involving customer data could result in hefty fines and irreparable damage to a company’s reputation.
Job Displacement and Workforce Adaptation
The automation potential of LLMs raises concerns about job displacement in various sectors. While LLMs can augment human capabilities and create new roles, some existing jobs might become obsolete. Companies need to proactively address this by investing in employee retraining and upskilling programs, focusing on skills that complement LLM capabilities, such as critical thinking, creativity, and complex problem-solving. Open communication with employees about the impact of LLMs and a commitment to supporting workforce transition are crucial for maintaining a positive and productive work environment.
Ethical Guidelines for Businesses Utilizing LLMs
Implementing LLMs responsibly requires a commitment to ethical principles. Businesses should adopt clear guidelines to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Transparency and Explainability: Clearly communicate to users how LLMs are being used and the potential limitations of their outputs.
- Data Privacy and Security: Implement robust data protection measures and comply with all relevant data privacy regulations.
- Bias Mitigation: Actively identify and mitigate biases in training data and LLM outputs.
- Accountability and Oversight: Establish clear lines of responsibility and implement mechanisms for monitoring and auditing LLM use.
- Human-in-the-Loop Systems: Maintain human oversight, especially in critical decision-making processes, to ensure responsible and ethical use.
- Fairness and Non-discrimination: Ensure that LLM applications do not discriminate against any individuals or groups.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental footprint of LLM training and deployment and strive for sustainable practices.
Future Trends and Predictions
The next five to ten years promise a dramatic reshaping of business landscapes, driven by the relentless evolution of large language models (LLMs). We’re not just talking incremental improvements; we’re on the verge of a paradigm shift where LLMs become integral to nearly every aspect of commerce, from product development to customer service and strategic decision-making. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the rapidly approaching reality fueled by advancements in AI and ever-increasing computational power.
LLMs will evolve significantly in the coming decade, moving beyond their current capabilities. Expect to see a marked increase in their reasoning abilities, enabling them to handle complex tasks requiring nuanced understanding and contextual awareness. We can anticipate improvements in handling multi-modal data, integrating text, images, audio, and video to create more holistic and intelligent systems. This will lead to a more seamless user experience and unlock entirely new applications previously unimaginable. Furthermore, the development of more efficient and cost-effective training methods will democratize access to these powerful tools, allowing smaller businesses to leverage LLM capabilities previously only available to tech giants.
LLM-Driven Business Model Innovation
The potential for LLMs to spawn entirely new business models is immense. Imagine personalized education platforms that adapt to individual learning styles in real-time, powered by LLMs that generate customized lesson plans and provide instant feedback. Or consider the rise of AI-driven creative agencies, where LLMs collaborate with human designers to generate innovative marketing campaigns and product designs at unprecedented speeds. The ability of LLMs to analyze vast datasets and identify emerging trends will empower businesses to proactively adapt to market changes and identify lucrative opportunities before their competitors. For example, a retail company could use an LLM to analyze social media trends and predict upcoming fashion styles, allowing them to optimize inventory and marketing campaigns accordingly, gaining a significant competitive advantage. This proactive, data-driven approach will become the new norm.
A Future Business Scenario: The AI-Powered Personalized Healthcare Provider
Consider “MediSage,” a future healthcare provider heavily reliant on advanced LLMs. MediSage uses sophisticated LLMs to analyze patient medical history, current symptoms, and the latest medical research to provide personalized treatment plans. The LLM acts as a virtual assistant, scheduling appointments, reminding patients about medication, and answering their health-related queries with accurate and up-to-date information. It can even analyze medical images and identify potential issues, assisting doctors in making faster and more accurate diagnoses. The societal impact is substantial: increased access to quality healthcare, particularly in underserved areas, improved patient outcomes through personalized care, and reduced healthcare costs through efficient resource allocation. However, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and algorithmic bias will need to be carefully addressed to ensure responsible and equitable implementation. MediSage’s success will depend on its ability to build trust and transparency, ensuring patients understand how their data is being used and that the LLM’s recommendations are always reviewed by human medical professionals.
Case Studies of Successful LLM Implementation

Source: turbotic.com
Large language models are rapidly transforming industries, but seeing is believing. This section dives into real-world examples of companies successfully integrating LLMs, showcasing their approaches, results, and hard-won lessons. These case studies illustrate the diverse applications of LLMs and offer valuable insights for businesses considering similar implementations.
Successful LLM Implementations Across Industries
The following table details three distinct companies and their experiences with LLMs. Each case study highlights a unique application and offers valuable lessons for businesses exploring LLM integration.
| Company | Implementation Details | Results | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | Grammarly leverages LLMs to power its grammar and writing assistance tools. Their implementation involves fine-tuning pre-trained models on vast datasets of written text to identify grammatical errors, stylistic issues, and tone inconsistencies. This allows for sophisticated suggestions and real-time feedback to users. | Significant improvements in user writing quality, increased user engagement and satisfaction, and expanded market reach. Grammarly has become a ubiquitous tool for writers across various professions. | The importance of high-quality training data is paramount. Continuous model retraining and refinement are crucial to maintain accuracy and adapt to evolving language use. Addressing ethical concerns regarding potential biases in the model is essential for long-term success. |
| Jasper | Jasper utilizes LLMs to provide AI-powered content generation services. Their platform enables users to create various types of marketing copy, blog posts, and other written content with minimal effort. Jasper’s implementation focuses on user-friendly interfaces and customization options to cater to diverse user needs. | Increased efficiency in content creation for businesses, reduced costs associated with hiring human writers, and improved content quality through automated optimization. Jasper has established itself as a leading player in the AI-powered content creation market. | Balancing creativity and accuracy in AI-generated content is crucial. Understanding user needs and providing tools for customization are key to user adoption. Maintaining data privacy and security is paramount in handling sensitive user information. |
| GitHub Copilot | GitHub Copilot uses LLMs to provide code completion and suggestion functionalities to developers. It analyzes code context and suggests relevant code snippets, helping developers write code faster and more efficiently. This implementation requires deep integration with coding environments and extensive training on vast repositories of code. | Increased developer productivity, improved code quality through automated suggestions, and reduced development time. Copilot has become a popular tool for developers across various programming languages. | Ensuring the accuracy and security of the generated code is crucial. Addressing potential copyright and intellectual property concerns related to training data is essential. Balancing automation with human oversight is key to avoid errors and maintain code quality. |
Best Practices for LLM Implementation, Large language models in business innovation
Based on these case studies, several best practices emerge for successful LLM implementation. Prioritizing data quality, ensuring model accuracy and ethical considerations, and continuously monitoring and refining the model are crucial for achieving optimal results. Furthermore, user experience and integration with existing workflows should be carefully considered to maximize adoption and impact. A strong emphasis on data privacy and security is also paramount.
Conclusion

Source: website-files.com
The integration of large language models into business is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s a rapidly unfolding reality. From automating mundane tasks to fueling groundbreaking innovation, LLMs are reshaping industries and creating unprecedented opportunities. While challenges remain – particularly regarding ethical considerations and responsible implementation – the potential rewards are undeniable. The companies that successfully navigate these complexities and embrace the transformative power of LLMs will be the ones leading the charge in the next generation of business.