Xctdoor malware attacking IIS servers? Yeah, it’s a real thing, and it’s way scarier than your last Tinder date gone wrong. This sneaky malware targets the vulnerabilities of Internet Information Services (IIS) servers, essentially the backbone of many websites. We’re diving deep into how it works, its devastating impact, and most importantly, how to protect yourself from this digital menace. Think of it as a cybersecurity thriller, but with less explosions and more… well, more data breaches.
We’ll break down Xctdoor’s functionality, its infection vectors, and the nasty payloads it delivers. We’ll also cover the specific vulnerabilities it exploits in IIS servers, showing you exactly how it gains access and wreaks havoc. Finally, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to detect, prevent, and remediate Xctdoor infections, so you can keep your servers safe and sound (and your data out of the wrong hands).
Understanding XCTDoor Malware: Xctdoor Malware Attacking Iis Servers
Source: thehackernews.com
XCTDoor is a sophisticated piece of malware primarily targeting Microsoft IIS servers. Its stealthy nature and ability to persist within a compromised system make it a significant threat to web servers and the data they hold. Understanding its functionality, infection vectors, and payloads is crucial for effective mitigation and remediation.
XCTDoor Malware Functionality
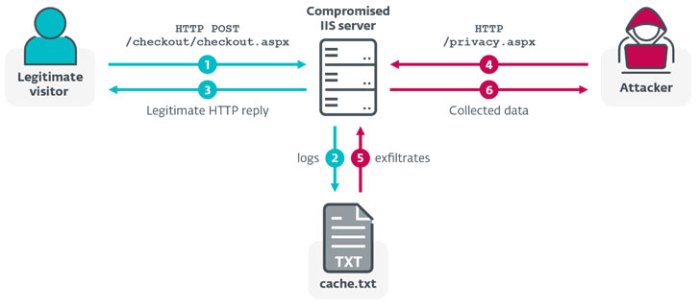
XCTDoor functions as a backdoor, granting remote attackers unauthorized access to the compromised server. Once installed, it establishes a persistent connection, allowing the attacker to execute commands, steal data, and further compromise the system. This access can be used for various malicious activities, including data exfiltration, deploying additional malware, and launching further attacks against other systems. The malware’s core functionality revolves around establishing and maintaining this persistent connection, often using obfuscation techniques to evade detection.
XCTDoor Infection Vectors
Infection typically occurs through vulnerabilities in the targeted IIS server. This could involve exploiting known security flaws in IIS components or leveraging vulnerabilities in web applications running on the server. Phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links are also a common infection vector, leading to the installation of XCTDoor through social engineering. Another potential method is through compromised third-party software or plugins integrated with the IIS server. The attacker leverages these vulnerabilities to gain initial access and then install the malware.
XCTDoor Payloads
The payloads delivered by XCTDoor vary depending on the attacker’s goals. Common payloads include additional malware that expands the attacker’s control over the compromised system. This could range from ransomware encrypting sensitive data to keyloggers capturing user credentials. Data exfiltration tools are frequently deployed to steal sensitive information, such as customer databases, financial records, or intellectual property. In some cases, XCTDoor itself acts as a payload, providing the attacker with a persistent backdoor for future operations.
XCTDoor Malware Architecture
XCTDoor’s architecture is typically modular, allowing for flexibility and adaptability. A core component manages the persistent connection and communication with the attacker’s command-and-control (C&C) server. Other modules handle specific tasks, such as data exfiltration, command execution, and self-preservation. This modular design allows attackers to easily update or modify the malware’s functionality without needing to rewrite the entire codebase. The communication with the C&C server is often encrypted and obfuscated to evade detection by security software.
XCTDoor Variants and Characteristics
Understanding the variations within XCTDoor is vital for effective defense. Different versions may utilize different techniques for persistence, communication, and payload delivery.
| Variant | Persistence Method | Communication Method | Payload |
|---|---|---|---|
| XCTDoor v1.0 | Registry Key Modification | HTTP | Data Exfiltration Tool |
| XCTDoor v2.0 | Scheduled Task Creation | HTTPS with SSL Encryption | Ransomware |
| XCTDoor v3.0 | Service Installation | DNS Tunneling | Keylogger and Remote Access Trojan (RAT) |
| XCTDoor v4.0 | DLL Injection | Obfuscated HTTP POST Requests | Custom Malware |
XCTDoor’s Targeting of IIS Servers
XCTDoor, a malicious piece of software, specifically targets Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) servers, leveraging known vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and establish a persistent foothold. Understanding its tactics is crucial for system administrators to bolster their defenses and prevent devastating attacks. This section delves into the specifics of XCTDoor’s targeting of IIS servers, examining its methods and impact.
XCTDoor’s attack methodology hinges on exploiting weaknesses in IIS configurations and outdated software. This isn’t a new approach; many successful malware campaigns exploit known vulnerabilities, and XCTDoor is no different. The effectiveness of these attacks often stems from organizations failing to implement timely security updates and maintain robust security practices.
Vulnerabilities Exploited by XCTDoor
XCTDoor commonly exploits vulnerabilities in older, unpatched versions of IIS. These vulnerabilities can range from insecure configurations allowing remote code execution to flaws in specific IIS components. The specific vulnerabilities leveraged often depend on the version of IIS targeted and the sophistication of the attack. Successful exploitation allows the malware to gain initial access to the server. For example, a known vulnerability might involve a poorly configured web application allowing for SQL injection, which XCTDoor then uses as an entry point.
Persistence Mechanisms Employed by XCTDoor
Once inside, XCTDoor utilizes various techniques to maintain persistent access to the compromised IIS server. This persistent presence allows the attackers to maintain control even after a server restart or other system changes. Common methods include creating scheduled tasks, modifying system registry entries, or installing backdoors within legitimate system processes. This persistent access allows for continued malicious activity, data exfiltration, or further attacks on other systems within the network.
Impact of XCTDoor Infections on IIS Server Functionality
The consequences of an XCTDoor infection on an IIS server can be severe. Depending on the attacker’s goals, the infection might lead to website defacement, data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, or the server being used as a launchpad for further attacks against other systems. Performance degradation is also common due to the malware’s resource consumption. In some cases, the infection might go unnoticed for extended periods, allowing attackers to conduct malicious activities undetected. This highlights the importance of regular security audits and monitoring.
Real-World Examples of XCTDoor Attacks
While specific details of XCTDoor attacks are often kept confidential for security reasons, numerous incidents have involved similar malware exploiting IIS vulnerabilities. News reports frequently detail large-scale attacks targeting organizations with outdated IIS servers, resulting in data breaches and financial losses. These incidents underscore the real-world threat posed by this type of malware and the importance of proactive security measures. For instance, a hypothetical scenario might involve a small business neglecting to update its IIS server, leading to an attack resulting in customer data being stolen.
Hypothetical XCTDoor Attack Scenario
Imagine a small e-commerce business running an outdated version of IIS without proper security patching. An attacker scans the internet for vulnerable servers, discovers the business’s server, and exploits a known vulnerability in the outdated IIS version. XCTDoor is successfully deployed, establishing persistence through a scheduled task. The attacker then uses the compromised server to exfiltrate customer credit card information and other sensitive data. This scenario demonstrates the potential consequences of neglecting basic security updates and practices.
Detection and Prevention Strategies
So, you’ve got a nasty XCTDoor malware infection lurking on your IIS servers. Not good. But don’t panic. Knowing how to detect and prevent these attacks is half the battle. This section dives into the practical steps you can take to secure your systems and keep those digital doors firmly locked.
Early detection and proactive prevention are crucial in combating XCTDoor. By understanding the telltale signs of an infection and implementing robust security measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to this malicious software.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying an XCTDoor infection requires a keen eye for suspicious activity. Several indicators can point to a compromise. These range from unusual network traffic patterns to the presence of specific files or registry entries associated with the malware. Prompt identification allows for quick containment and remediation.
Look out for unusual file creations in your IIS directories, especially those with seemingly random names or extensions. Monitor network traffic for connections to known malicious IP addresses or domains. Unexpected changes to web.config files or other IIS configuration settings should also raise red flags. Finally, performance degradation or uncharacteristic server behavior can indicate a hidden infection.
Security Best Practices for Preventing XCTDoor Attacks
Preventing XCTDoor attacks starts with strong security fundamentals. This involves a multi-layered approach combining regular patching, strong password policies, and rigorous access control. Think of it as building a fortress around your IIS servers, making it as difficult as possible for attackers to breach your defenses.
Regularly update your IIS server software and all related components with the latest security patches. Implement strong password policies, enforcing complexity and regular changes. Restrict access to your IIS server using the principle of least privilege. Only grant access to necessary users and services. Keep your operating system and all applications updated with the latest security patches.
The Role of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS systems act as vigilant guards, constantly monitoring network traffic and system activity for malicious behavior. They can detect suspicious patterns indicative of an XCTDoor attack, such as unauthorized file access or unusual network connections. A well-configured IDPS can provide real-time alerts and even automatically block malicious activity before it causes significant damage.
Deploy an IDPS that’s capable of analyzing web server logs and network traffic for known XCTDoor signatures and suspicious behavior. Regularly review the IDPS logs to identify potential threats and adjust your security measures accordingly. Configure your IDPS to generate alerts for suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts, unusual file modifications, or excessive resource consumption.
Regular Security Audits for XCTDoor Detection
Regular security audits are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. They provide a systematic way to assess your security controls, identify vulnerabilities, and detect potential infections. Think of them as comprehensive health checks for your IIS servers, helping to catch problems before they escalate.
Conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify potential weaknesses in your IIS server configuration. Perform regular security audits to review your security controls and detect any anomalies or vulnerabilities. Employ penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify potential vulnerabilities. Regularly review server logs for any suspicious activity that might indicate a compromise.
Recommended Security Tools and Techniques
Several tools and techniques can enhance your defenses against XCTDoor. These range from robust antivirus solutions to web application firewalls (WAFs) and regular security assessments. A layered approach offers the best protection.
Implement a robust antivirus solution on your IIS servers to detect and remove malware. Use a web application firewall (WAF) to filter malicious traffic and protect against web-based attacks. Regularly back up your server data to ensure you can recover from a compromise. Employ a security information and event management (SIEM) system to collect and analyze security logs from various sources.
Remediation and Response

Source: phishprotection.com
Facing an XCTDoor infection on your IIS server is a serious situation demanding swift and decisive action. The longer the malware remains active, the greater the risk of data breaches, system instability, and long-term damage to your organization’s reputation and operations. Effective remediation requires a structured approach, combining technical expertise with a well-defined incident response plan.
Remediating an XCTDoor infection involves a multi-stage process that prioritizes containment, eradication, recovery, and prevention. Failure to address each stage thoroughly increases the likelihood of re-infection and persistent vulnerabilities. This section Artikels the critical steps involved in restoring infected IIS servers to a clean and secure state.
IIS Server Remediation Steps
The remediation process begins with isolating the infected server to prevent further spread. This involves disconnecting it from the network, disabling any unnecessary services, and blocking inbound and outbound connections. Next, a comprehensive backup of the server’s state (before any cleanup attempts) should be created to facilitate recovery if necessary. Then, malware removal tools should be employed to eliminate the XCTDoor payload and associated files. Finally, a thorough system scan and patching process should be implemented to close any identified vulnerabilities exploited by the malware. Regular system updates and security patches are essential for preventing future attacks.
Restoring Infected IIS Servers
Restoring an infected IIS server to a clean state involves several key steps. First, a clean installation of the operating system is often the most effective method, ensuring complete removal of the malware and any lingering artifacts. Following the OS reinstallation, all necessary IIS components and applications should be reinstalled from trusted sources. Before restoring any data from backups, those backups themselves should be scanned for malware to avoid reinfection. Once the system is verified as clean, data restoration can proceed, focusing on the most critical and recently backed-up files first.
Incident Response Planning for XCTDoor Attacks
A robust incident response plan is crucial for effectively managing XCTDoor attacks. This plan should detail procedures for detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing should be incorporated to proactively identify and address potential weaknesses. The plan should also include communication protocols for informing stakeholders and regulatory bodies, as required. Regular drills and simulations are essential for ensuring the plan’s effectiveness and for training personnel. For example, a realistic scenario could simulate a widespread XCTDoor infection across multiple servers, testing the team’s ability to contain the outbreak and restore systems quickly.
Forensic Analysis Techniques
Forensic analysis plays a vital role in understanding the extent of the XCTDoor infection and identifying the attacker’s methods. This involves collecting and analyzing system logs, network traffic data, and malware samples. Memory forensics can be employed to capture volatile data that may not be preserved on the hard drive. Analyzing the malware’s code can reveal its functionalities, communication channels, and command-and-control infrastructure. Network analysis can identify the source of the attack and the extent of data exfiltration. For example, examining IIS logs may reveal unusual access patterns or suspicious requests originating from compromised systems.
Data Recovery from XCTDoor Compromise
Recovering data compromised by XCTDoor requires a careful approach. If a clean backup exists that predates the infection, restoring from this backup is the most reliable method. However, if the backups are compromised, data recovery tools and techniques may be needed. These tools can often recover deleted or overwritten files, but success depends on the extent of the damage and the tools used. It’s crucial to prioritize the recovery of the most critical data first. For instance, recovering customer databases or financial records should take precedence over less critical data. The recovery process may involve working with data recovery specialists if the damage is extensive.
Vulnerability Analysis and Patching
XCTDoor’s success hinges on exploiting vulnerabilities in IIS servers. Understanding these weaknesses and implementing robust patching strategies is crucial for preventing infection and maintaining a secure server environment. This section delves into the common vulnerabilities, the importance of regular updates, and practical steps for effective vulnerability management.
IIS servers, like any software, are susceptible to various security flaws. Regular patching and updates are not merely a good practice; they are a fundamental requirement for preventing attacks like those launched by XCTDoor. Ignoring these updates leaves your server exposed to known exploits, making it a prime target for malicious actors.
Common IIS Vulnerabilities Exploited by XCTDoor
XCTDoor often leverages known vulnerabilities in IIS components to gain unauthorized access. These vulnerabilities can range from outdated software versions with known security flaws to misconfigurations that allow for unauthorized access. For instance, unpatched versions of IIS might contain flaws in their handling of specific file types or HTTP requests, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code or gain control of the server. Another common vulnerability is the improper configuration of access control lists (ACLs), permitting unauthorized users to access sensitive files or directories.
The Importance of Regular Patching and Updates for IIS Servers
Regular patching is paramount for maintaining the security of IIS servers. Microsoft regularly releases security updates addressing known vulnerabilities. These updates often include critical fixes that patch security holes actively exploited by malware like XCTDoor. Delaying or neglecting these updates significantly increases the risk of a successful attack. Imagine a scenario where a critical patch addressing a specific vulnerability exploited by XCTDoor is released, but an organization delays applying it. This delay directly exposes the server to potential compromise. The consequences can range from data breaches and financial losses to reputational damage and legal repercussions.
Applying Security Patches to Mitigate XCTDoor Vulnerabilities
Applying security patches involves several steps. First, identify the specific vulnerabilities affecting your IIS server. This can be done through vulnerability scanning tools or by checking Microsoft’s security advisories. Next, download the relevant patches from the Microsoft Update Catalog or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). Before applying the patches, it’s crucial to back up your server configuration. Finally, install the patches following Microsoft’s instructions, carefully reviewing any potential downtime or service interruptions. Post-patching, it’s essential to verify the successful application of the patches and retest the server’s functionality to ensure no unexpected issues have arisen.
Different Approaches to Vulnerability Management for IIS Servers
Several approaches exist for managing IIS server vulnerabilities. These range from manual patching and updates to employing automated vulnerability scanning and patching tools. Manual patching requires meticulous attention to detail and can be time-consuming. Automated tools, however, streamline the process, regularly scanning for vulnerabilities and automatically applying patches. The choice depends on the organization’s resources and technical expertise. Larger organizations often benefit from automated solutions, while smaller organizations might opt for a more manual approach. A hybrid approach, combining automated scanning with manual verification, offers a balanced solution.
Proactive Vulnerability Management Plan to Prevent Future XCTDoor Attacks, Xctdoor malware attacking iis servers
A proactive vulnerability management plan involves several key elements. Regular vulnerability scanning should be implemented, utilizing both automated tools and manual checks. This helps identify potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited. A strict patching schedule should be established and adhered to, prioritizing critical security updates. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address any weaknesses in the server’s security posture. Employee training is also crucial, educating staff on safe browsing habits and recognizing phishing attempts. Finally, implementing a robust incident response plan ensures a quick and effective response in case of a successful attack. This plan should Artikel steps for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Outcome Summary

Source: amazonaws.com
So, the bottom line? Xctdoor malware is a serious threat to IIS servers, but armed with the right knowledge and proactive security measures, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember, regular patching, robust security audits, and a solid incident response plan are your best defenses. Don’t wait until it’s too late; proactive security is the only way to stay ahead of these digital bad guys. Think of it as your cybersecurity insurance policy – and nobody wants to be the one left uninsured when disaster strikes.