Google Chrome to block Entrust SSL? Yeah, we’re diving deep into the surprisingly complex world of website security. It’s not just about pretty padlock icons; sometimes, you need to take control of which SSL certificates your browser trusts. This isn’t your grandma’s internet anymore; we’re talking about actively managing your online safety, one SSL certificate at a time. This guide will walk you through why you might want to block Entrust SSL certificates in Chrome, how to do it, and what to watch out for.
We’ll cover everything from understanding the different types of Entrust SSL certificates and the potential security risks associated with them, to the various methods for blocking them in Chrome – from tweaking built-in settings to using extensions and even enterprise management systems. We’ll also explore alternative solutions and troubleshoot common problems, ensuring you’re equipped to navigate the sometimes-murky waters of online security.
Understanding Entrust SSL Certificates
Entrust Datacard, now part of Entrust, is a major player in the digital security world, offering a range of SSL certificates to secure websites and online transactions. These certificates are crucial for establishing trust between a website and its visitors, ensuring data transmitted between the two is encrypted and protected from prying eyes. Understanding how they function and the different types available is key to appreciating their role in maintaining a secure online environment.
Entrust SSL certificates work by using public key cryptography. The website owner obtains a certificate from Entrust, which includes a public key. This public key is used to encrypt data sent from the user’s browser to the website. The website, in possession of the corresponding private key, can then decrypt this data. This process ensures that sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, and personal data remain confidential during transmission. The certificate also verifies the website’s identity, preventing malicious actors from impersonating legitimate sites. This verification process involves checking the website’s ownership and legitimacy through a rigorous validation process.
Entrust SSL Certificate Types
Entrust offers a variety of SSL certificates catering to different needs and security levels. The choice depends on factors like the website’s complexity, the level of security required, and the budget. Each certificate type offers a different level of validation and security features.
Examples of Websites Using Entrust SSL Certificates
While Entrust doesn’t publicly list all its clients, it’s safe to say many large organizations and businesses rely on Entrust’s SSL certificates for their security needs. Given Entrust’s market position, it’s highly probable that many websites you visit daily, especially those handling sensitive financial or personal data, use Entrust certificates. Consider major banks, e-commerce platforms, and government websites – these are all likely candidates that prioritize robust security solutions provided by established players like Entrust. The specific examples would require access to private client lists which are not publicly available.
Reasons for Blocking Entrust SSL Certificates in Chrome
Source: templatemela.com
Chrome’s decision to block certain Entrust SSL certificates isn’t arbitrary; it’s a proactive measure to safeguard user data and maintain a secure browsing experience. These blocks are triggered by specific security vulnerabilities or breaches of trust that compromise the integrity of the certificate’s verification process. Understanding these reasons is crucial for appreciating Chrome’s commitment to online security.
The primary reason behind blocking specific Entrust SSL certificates stems from identified weaknesses in their cryptographic infrastructure or the certificate issuance process itself. This can involve flaws in the algorithms used, compromised private keys, or procedural issues leading to the illegitimate issuance of certificates. Such weaknesses leave websites vulnerable to various attacks, potentially allowing malicious actors to intercept sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
Security Risks Associated with Specific Entrust SSL Certificates
Compromised Entrust certificates can create several serious security risks. A compromised certificate allows an attacker to impersonate a legitimate website, intercepting communications and potentially stealing sensitive user data. For instance, a malicious actor could obtain a certificate for a banking website, creating a fraudulent site indistinguishable from the genuine one. Users connecting to this fraudulent site would unknowingly transmit their credentials directly to the attacker. Another scenario involves the use of weak cryptographic algorithms in the certificate, making it vulnerable to cracking, thus rendering the encryption useless and exposing communications. The severity of the risk depends on the specific vulnerability and the sensitivity of the data being transmitted. A compromised certificate for a social media site might expose personal information, while a compromised certificate for an e-commerce site could lead to financial fraud.
Scenarios Requiring Blocking Entrust SSL Certificates
Blocking is necessary when a significant security flaw is discovered within the Entrust certificate infrastructure or when a certificate is found to have been issued improperly. This could involve situations where a private key used to sign certificates has been compromised, allowing for the creation of fraudulent certificates. Another scenario involves the discovery of vulnerabilities in the certificate generation or validation process itself, leading to the potential for fraudulent certificates to be issued undetected. In such cases, Chrome’s action of blocking affected certificates is a critical step in preventing widespread exploitation and protecting users from potential harm. For example, if a large number of certificates were issued using a compromised key, blocking them would prevent attackers from using those certificates to impersonate legitimate websites.
Comparison of Security Implications: Blocking vs. Allowing Entrust SSL Certificates
Allowing compromised Entrust SSL certificates exposes users to significant risks, including man-in-the-middle attacks, data breaches, and identity theft. Conversely, blocking these certificates prevents these attacks by ensuring that users are not connected to websites using compromised certificates. While blocking might cause temporary inconvenience for users accessing websites with legitimate but affected certificates, this inconvenience is far outweighed by the significant security risks associated with allowing these certificates. The decision to block is therefore a calculated risk assessment, prioritizing user security over temporary accessibility issues. The potential damage from a data breach far exceeds the inconvenience of a temporary website inaccessibility.
Methods to Block Entrust SSL Certificates in Chrome
So, you’ve decided you want to block Entrust SSL certificates in Chrome. Maybe you’re concerned about security vulnerabilities, or perhaps you’re dealing with specific website issues. Whatever the reason, let’s explore the different ways you can achieve this. We’ll cover methods ranging from simple built-in Chrome settings to more advanced techniques.
Blocking Entrust SSL Certificates Using Chrome’s Built-in Settings
Blocking Entrust certificates directly through Chrome’s built-in settings isn’t a straightforward process. Chrome doesn’t offer a granular option to blacklist specific Certificate Authorities (CAs) like Entrust. However, you can achieve a similar result by manipulating Chrome’s settings to disable all untrusted certificates. This is a less precise method, as it will block all certificates not explicitly trusted by Chrome, but it can be effective in certain scenarios. Remember that this method may break legitimate websites that rely on certificates not included in Chrome’s default trust store. Proceed with caution.
- Open Chrome’s settings. You can usually do this by clicking the three vertical dots in the upper right corner of the browser window and selecting “Settings”.
- Navigate to “Privacy and security”.
- Click on “Security”.
- Under “Manage certificates,” click on “View certificates”.
- Explore the options within this section. Unfortunately, there’s no direct method to remove or blacklist Entrust. The closest you can get is to review and potentially remove certificates you don’t recognize, although this is a manual and time-consuming process and may not completely address the issue.
Using Extensions to Block Specific SSL Certificates, Google chrome to block entrust ssl
Chrome extensions provide a more flexible approach to managing SSL certificates. While there isn’t a widely known extension specifically designed to blacklist Entrust, you can use extensions that allow you to manage and block certificates based on various criteria, such as the issuer or specific certificate fingerprints. These extensions often require advanced technical knowledge to use effectively.
| Name | Description | Functionality | Installation |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Hypothetical Extension A) | A hypothetical extension allowing granular control over SSL certificates. | Allows users to specify criteria for blocking certificates, such as issuer name or certificate fingerprint. Could potentially be used to block Entrust certificates. | Install from the Chrome Web Store (if such an extension existed). |
| (Hypothetical Extension B) | Another hypothetical extension focused on security and certificate management. | Offers advanced features for managing certificates, including the possibility of blacklisting specific CAs. Requires technical expertise to configure. | Install from the Chrome Web Store (if such an extension existed). |
Implementing a Custom Certificate Blacklist in Chrome’s Enterprise Management System
For organizations managing Chrome deployments through an enterprise management system (like Google Workspace or Microsoft Intune), implementing a custom certificate blacklist is the most effective and precise method. This involves configuring policies within the management console to explicitly block certificates issued by Entrust. This approach requires administrator privileges and familiarity with the specific enterprise management system being used. The exact steps vary depending on the system, but generally involve creating a policy that defines the blocked certificates using specific criteria like issuer name or certificate fingerprints. This policy is then deployed to the managed Chrome instances.
Alternatives to Blocking Entrust SSL Certificates

Source: otechworld.com
Completely blocking an entire Certificate Authority like Entrust might seem like a drastic, albeit seemingly secure, solution. However, it disrupts access to legitimate websites and services that rely on Entrust certificates. A more nuanced approach involves carefully managing the risks associated with these certificates instead of outright rejection. This allows for a balance between security and functionality.
Let’s explore alternative strategies that prioritize security without sacrificing access to necessary online resources. These methods offer a more granular control over how Chrome handles Entrust certificates, allowing you to address specific concerns rather than implementing a blanket ban.
Certificate Pinning
Certificate pinning is a technique where a website’s developers embed the expected public key of their SSL certificate directly into their application. This means that the browser will only trust the certificate if it matches the pinned key, effectively bypassing the reliance on the Certificate Authority entirely. If a malicious certificate is presented, the connection will fail. This offers strong protection against man-in-the-middle attacks, specifically targeting the websites you’ve pinned. Implementing certificate pinning requires cooperation from the website developers, making it less of a user-level solution.
Enhanced Security Settings and Exceptions
Chrome offers granular control over its security settings. Instead of blocking all Entrust certificates, you can configure Chrome to display warnings for certificates issued by Entrust that have raised security flags, such as expired certificates or those with compromised private keys. This allows users to make informed decisions about whether to proceed with a connection. You can also add exceptions for specific websites using Entrust certificates that you trust, allowing you to continue accessing them without facing a blanket block. This requires vigilance and careful consideration of the risks involved for each website. It’s a middle ground, trading automatic security for informed user decision-making.
Using a Different Browser or Extension
While not a direct solution for managing Entrust certificates within Chrome, switching to a different browser or using a browser extension that offers enhanced SSL/TLS management capabilities could provide an alternative. Some browsers might have different default settings or extensions that allow for more fine-grained control over certificate handling. This approach isn’t about fixing Chrome’s handling of Entrust certificates, but rather providing an alternative route to accessing websites that use them. However, it doesn’t solve the underlying issue of potentially compromised Entrust certificates. The efficacy of this method relies heavily on the security features of the alternative browser or extension.
Comparison of Approaches
The choice of approach depends heavily on the user’s technical expertise and risk tolerance. Here’s a comparison:
- Blocking Entrust Certificates (Least Granular): Simple to implement, but disrupts access to many legitimate websites. High risk of breaking functionality.
- Certificate Pinning (Most Granular): Highly secure but requires developer cooperation. Limited to specific websites.
- Enhanced Security Settings and Exceptions (Medium Granularity): Offers a balance between security and functionality, requiring user vigilance.
- Using a Different Browser/Extension (Medium Granularity): Provides an alternative, but doesn’t address the root problem directly. Relies on the security of the alternative.
Troubleshooting and Error Handling
Source: amazonaws.com
Blocking Entrust SSL certificates in Chrome, while seemingly straightforward, can sometimes throw a wrench in the works. Unexpected errors can pop up, leaving you scratching your head. Understanding these potential pitfalls and knowing how to address them is crucial for a smooth, secure browsing experience. This section details common issues and provides practical solutions to get you back on track.
Troubleshooting these errors often involves a combination of checking Chrome’s settings, verifying extensions, and potentially resetting your browser profile. Remember, always back up your important data before making significant changes to your browser configuration.
Common Errors and Solutions
Let’s dive into some common problems encountered while attempting to block Entrust SSL certificates and their respective solutions. These errors usually stem from misconfigurations in Chrome’s settings or interference from browser extensions.
| Error | Cause | Solution | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome continues to connect to sites using Entrust certificates despite blocking attempts. | Incorrectly configured Chrome settings or interference from a browser extension overriding the block. | Carefully review your Chrome settings, particularly those related to certificate management and extensions. Disable extensions temporarily to isolate the culprit. If necessary, reset Chrome to its default settings (this will erase your browsing data, so back it up!). | Ensure you’re using the correct method for blocking certificates, as described in previous sections. Double-check for typos in any manually entered certificate details. |
| Error message indicating a certificate is not trusted, even after blocking. | The certificate might not be managed by Chrome’s certificate store or the blocking method isn’t effective for that specific certificate. | Verify the certificate is indeed within the scope of your blocking method. Ensure the certificate is properly identified and targeted for blocking. Consider using alternative methods for blocking if necessary. | Some certificates may be deeply integrated into the system, requiring more advanced techniques beyond simple Chrome settings modification. |
| Websites fail to load entirely after attempting to block Entrust certificates. | Overly aggressive blocking rules that inadvertently block legitimate certificates or essential website components. | Review your blocking rules to ensure they are specific to Entrust certificates and don’t inadvertently target other necessary certificates. Temporarily disable the blocking rules to see if the websites load correctly. If they do, refine your blocking rules gradually. | This error highlights the importance of precision when blocking certificates. A broad approach can disrupt browsing functionality. |
| Chrome crashes or becomes unresponsive after implementing certificate blocking. | A conflict between the blocking method and other Chrome extensions or settings. | Restart Chrome. If the issue persists, disable extensions one by one to identify the conflicting extension. Consider resetting Chrome to its default settings (remember to back up your data). | This error suggests a significant conflict. System-level issues could also be at play; consider restarting your computer. |
Security Implications and Best Practices
Blocking specific SSL certificate authorities like Entrust, while seemingly offering a targeted security solution, carries broader implications for overall online security. It’s a delicate balancing act: while aiming to mitigate certain risks, such actions can inadvertently introduce new vulnerabilities or hinder legitimate website access. Understanding these implications and adopting best practices is crucial.
The act of selectively blocking certificate authorities disrupts the established trust model of the internet. This can lead to websites using legitimate Entrust certificates being incorrectly flagged as insecure, hindering user access to essential services and potentially impacting business operations. Furthermore, it can create a false sense of security, as it doesn’t address the root causes of potential security breaches. A holistic approach, focusing on broader security measures, is far more effective.
The Risks of Blocking Certificate Authorities
Blocking a CA like Entrust could lead to several unintended consequences. Users might lose access to websites legitimately using Entrust certificates, impacting their ability to conduct online banking, shopping, or access other crucial services. This can also negatively affect businesses relying on these certificates for secure transactions and communication. Moreover, such actions can create a breeding ground for phishing and other malicious activities, as legitimate websites might be mistakenly identified as insecure, driving users to less secure alternatives. A comprehensive approach to security, rather than isolated blocking measures, is the more responsible strategy.
Best Practices for Managing SSL Certificates
Effective SSL certificate management is paramount for online security. Regularly reviewing and updating certificates is crucial, ensuring they haven’t expired and are still considered valid by browsers. Using strong encryption protocols and employing robust security practices across all systems involved are also essential. Employing multi-factor authentication where possible, regularly backing up data, and keeping all software up-to-date, including operating systems and security applications, further enhances security.
Importance of Regularly Updating Chrome and its Security Settings
Chrome’s automatic update feature is a critical component of maintaining its security. Regular updates deliver vital security patches, addressing vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Users should ensure this feature is enabled and that updates are installed promptly. Additionally, regularly reviewing and adjusting Chrome’s security settings, such as enabling enhanced protection against phishing and malware, strengthens the browser’s defenses. These measures collectively contribute to a safer online experience. Ignoring updates leaves systems vulnerable to known exploits, which can have significant consequences. For example, the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 exploited a known vulnerability in older versions of Windows, causing widespread disruption and data loss. This highlights the importance of timely updates.
Visual Representation of the Blocking Process
When Chrome blocks an Entrust SSL certificate, it doesn’t silently fail. Instead, it presents a clear and unmistakable warning to the user, preventing them from accessing the website in question. This visual cue is crucial for user safety and understanding.
The visual changes are designed to immediately grab the user’s attention, making it impossible to miss the security issue. This ensures users aren’t inadvertently exposed to potentially malicious websites. The browser’s approach is consistent, ensuring a uniform user experience regardless of the specific website.
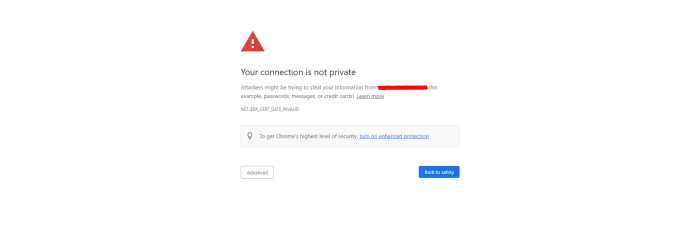
Error Message and Warning Display
Chrome will prominently display an error message in the address bar, usually a red or orange warning triangle. This is often accompanied by a descriptive text message clearly explaining why the connection is blocked. The message might say something like “Your connection is not private” or “NET::ERR_CERT_INVALID,” accompanied by an explanation that the site’s security certificate is not trusted by Google Chrome due to issues with the Entrust certificate. The text is typically straightforward and easily understandable, even for non-technical users. This is accompanied by a visual warning icon. The specific wording might vary slightly depending on the Chrome version and the precise nature of the certificate issue.
Visual Indicators in the Address Bar
Beyond the error message, the address bar itself might change visually. The typically green padlock icon, indicating a secure connection, will likely be absent or replaced with a red cross or a similarly alarming visual indicator. This change provides an immediate visual cue that something is wrong, even before the user reads the detailed error message. The color change (from green to red) is instantly recognizable as a warning signal. This immediate visual feedback is critical in enhancing user awareness of the security threat.
Website Display and User Interaction
The website itself will not load. Instead of the expected content, users will see the error page displayed by Chrome. This error page usually contains further details about the certificate problem, links to relevant help pages, and options to proceed at their own risk (though this option should be used with extreme caution). The inability to interact with the website’s content reinforces the severity of the security issue and discourages users from bypassing the warning. This prevents accidental exposure to potentially harmful content.
Wrap-Up: Google Chrome To Block Entrust Ssl
So, there you have it – a deep dive into the world of blocking Entrust SSL certificates in Google Chrome. While it might seem like a niche topic, understanding how to manage your browser’s security settings is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Remember, online security is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. Stay updated on the latest security threats, regularly update your browser and extensions, and always be mindful of the websites you visit. Mastering the art of SSL certificate management is one more step toward a safer online experience.



