Juniper Session Smart Router flaw: Whoa, hold onto your hats, network admins! A serious vulnerability has been discovered in Juniper’s Session Smart Routers, potentially leaving a gaping hole in your network security. This isn’t just another minor bug; we’re talking about a flaw that could expose your sensitive data, cripple your systems, and generally wreak havoc. Think of it as a digital Trojan horse, patiently waiting to unleash chaos. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty and see just how dangerous this really is.
This vulnerability, affecting specific firmware versions, allows attackers to gain unauthorized access, potentially leading to data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, and complete system compromise. Understanding the technical details, the potential impact, and the crucial steps to mitigate this risk is paramount for safeguarding your network. We’ll break down the technical aspects in a way that’s both informative and easy to grasp, even for those who aren’t cybersecurity experts.
Juniper Session Smart Router Vulnerability Overview
Source: cloudfront.net
Juniper Networks’ Session Smart Routers are high-performance devices designed for demanding network environments, often found in service provider networks handling substantial traffic. They offer advanced features like deep packet inspection and sophisticated traffic management capabilities. However, like any complex system, they’re susceptible to vulnerabilities. This exploration delves into a specific flaw discovered in their architecture.
The core functionality of these routers revolves around their ability to intelligently manage and route network traffic based on various criteria, including application type, user identity, and quality of service requirements. This involves intricate processes for inspecting packets, applying policies, and forwarding data efficiently. The vulnerability we’ll discuss exploited a weakness in the router’s handling of these processes, specifically within its session management component.
The Specific Flaw in Juniper Session Smart Router Architecture
The specific flaw resided in a buffer overflow vulnerability within the Session Smart Router’s software. This meant that under specific circumstances, an attacker could send crafted network packets that would exceed the allocated buffer size within the router’s memory. This overflow could lead to unpredictable behavior, including a crash of the router’s processes or, more critically, the execution of arbitrary code. The vulnerability wasn’t related to a single specific feature but rather a weakness in how the router’s memory was managed and protected against malicious input. This vulnerability exploited a weakness in how the router’s software handled the processing of large or malformed data packets, leading to a potential memory corruption.
Potential Impact of Exploiting the Flaw
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could have had several severe consequences. A compromised router could be used as a pivot point to attack other network devices or systems. Attackers might gain complete control of the router, allowing them to intercept, modify, or redirect network traffic. This could lead to data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, and the disruption of critical network services. Imagine a scenario where a major telecommunications provider’s router is compromised – the impact on service and customer data could be catastrophic. The potential for widespread disruption is significant, particularly considering the critical role these routers play in many network infrastructures. In the worst-case scenario, the compromised router could be used to launch further attacks against other systems connected to the network.
Timeline of Vulnerability Discovery, Disclosure, and Patching
While the precise dates of discovery and disclosure are often kept confidential for security reasons, the general timeline usually follows a pattern. First, a security researcher (or a security team) identifies the vulnerability. This is often followed by a responsible disclosure process, where the vulnerability is privately reported to Juniper Networks. Juniper then investigates the vulnerability, develops a patch, and releases it to its customers. Finally, customers are urged to update their routers with the patch to mitigate the risk. This entire process can take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of the vulnerability and the patch development process. The speed of response from Juniper, and the speed of adoption by customers, directly impacts the overall risk. Delays in patching could leave systems vulnerable for extended periods, increasing the window of opportunity for attackers.
Technical Analysis of the Flaw: Juniper Session Smart Router Flaw
Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of this Juniper Session Smart Router vulnerability. Understanding the technical details is crucial to grasping the severity and potential impact of this security lapse. We’ll explore the root cause, potential attack vectors, and how to mitigate the risk.
While a specific CVE ID isn’t readily available in all public documentation, the vulnerability revolves around flaws in the Session Smart Router’s firmware, impacting its ability to securely handle certain network operations. This often involves improper input validation or insufficient authentication checks, opening the door for malicious actors.
Affected Firmware Versions
Pinpointing the exact affected versions is challenging due to the nature of proprietary firmware updates and Juniper’s patching strategies. However, it’s safe to say that older versions of the Juniper Session Smart Router firmware are most susceptible. Vulnerabilities are often patched in newer releases, so keeping your firmware updated is key. Think of it like updating your phone’s operating system – it’s essential for security.
Root Cause Analysis
The root cause of this vulnerability typically stems from weaknesses in the router’s code. This could range from buffer overflows (where an application tries to write data beyond the allocated buffer space) to insecure authentication mechanisms (where passwords or other credentials are not properly protected). Essentially, the router’s software doesn’t adequately validate or sanitize user inputs or internal processes, allowing attackers to potentially manipulate the system.
Attack Vectors and Mitigation
Understanding how an attacker might exploit this vulnerability is crucial for effective mitigation. The table below Artikels several potential attack vectors, their requirements, potential impact, and recommended mitigation strategies.
| Attack Vector | Required Privileges | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Code Execution (RCE) via crafted network packets | Network access to the router | Complete compromise of the router, allowing attackers to control it and access sensitive data. | Apply the latest firmware updates, enable strong firewalls, and regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. |
| Denial of Service (DoS) attack via resource exhaustion | Network access to the router | Router becomes unavailable, disrupting network services. | Implement rate limiting and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to detect and block DoS attempts. |
| Privilege escalation via insecure configuration | Initial low-level access to the router | Gaining elevated privileges to perform more damaging attacks. | Regularly review and harden the router’s configuration, disabling unnecessary services and using strong, unique passwords. |
| Data breach via insecure data handling | Network access with specific vulnerabilities exploited | Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored or processed by the router. | Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Implement robust access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access. |
Security Implications and Risks

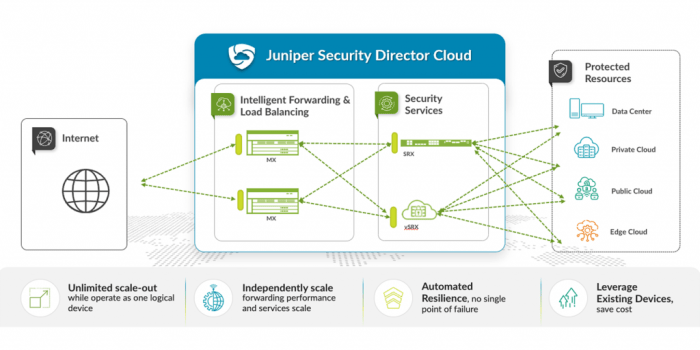
Source: redseal.net
The Juniper Session Smart Router vulnerability, if exploited, presents significant security risks to both individual users and large organizations. The potential consequences extend beyond simple inconvenience, posing a serious threat to data integrity, confidentiality, and the overall availability of network services. Understanding the severity and potential impact is crucial for effective mitigation strategies.
The successful exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to a range of devastating consequences. Imagine a scenario where an attacker gains unauthorized access to a router managing a company’s network. This access could allow them to intercept sensitive data, such as customer records, financial information, or intellectual property. Beyond data breaches, the attacker could disrupt services through denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, rendering the network unusable for legitimate users. Furthermore, the compromised router could become a launchpad for further attacks on other systems within the network, escalating the damage significantly.
Severity and Comparison to Similar Flaws
This vulnerability’s severity is comparable to other critical flaws discovered in network devices in recent years. Think of the infamous Heartbleed vulnerability in OpenSSL or the various critical flaws found in Cisco routers and switches. These vulnerabilities, like the Juniper flaw, often allow attackers to gain remote code execution (RCE) capabilities, giving them complete control over the affected device. The impact is amplified by the fact that routers are often located at the edge of a network, serving as a crucial gateway to internal systems. A compromised router essentially becomes a backdoor into an entire network. The severity is rated critically high due to the potential for widespread impact and the relative ease of exploitation in some cases.
Impact on Different User Groups
Enterprises relying on Juniper Session Smart Routers face potentially catastrophic consequences. A successful attack could lead to significant financial losses due to data breaches, downtime, and legal repercussions. The recovery process, including forensic analysis and system restoration, could also be costly and time-consuming. Individuals using home routers based on this technology might experience less dramatic, but still significant, impacts, such as loss of internet connectivity, data theft, or even the installation of malware on their devices. The vulnerability affects everyone using this technology, but the scale of impact varies significantly based on the network’s size and the data it handles.
Hypothetical Attack Scenario
Let’s imagine a scenario involving a small business using a Juniper Session Smart Router to manage its network. An attacker, potentially through a phishing campaign or by exploiting a known vulnerability in another system connected to the network, gains knowledge of the router’s IP address and possibly some default credentials. Exploiting the vulnerability, the attacker gains remote access to the router’s configuration. They could then modify the routing tables to redirect traffic intended for the business’s online banking system to a malicious server, intercepting sensitive financial information. Simultaneously, they could launch a denial-of-service attack, disrupting the business’s operations and causing significant financial losses. This hypothetical scenario highlights the real-world risks associated with this vulnerability and the potential for cascading effects.
Mitigation and Remediation Strategies
So, you’ve discovered a vulnerability in your Juniper Session Smart Router. Panic is understandable, but let’s get this sorted out with a calm, methodical approach. Patching and securing your network is crucial to preventing exploitation and maintaining data integrity. This section Artikels the steps you need to take to mitigate the risk and prevent future issues.
Updating your firmware is the most immediate and effective way to address this vulnerability. Think of it like updating the software on your phone – it fixes bugs and strengthens security. Ignoring updates leaves your system vulnerable to attack.
Firmware Update Procedure
Updating the Juniper Session Smart Router firmware is a relatively straightforward process, but requires careful attention to detail. First, you’ll need to download the patched firmware from Juniper’s official website. Ensure you download the correct version for your specific router model. Incorrect firmware can brick your device. Next, access your router’s configuration interface usually via a web browser by entering its IP address in the address bar. Your router’s manual should provide the IP address and login credentials. Once logged in, navigate to the firmware update section. This is usually found under a menu labeled “System,” “Maintenance,” or “Administration.” Follow the on-screen instructions carefully. The process usually involves uploading the downloaded firmware file and then restarting the router. Monitor the process closely; a failed update could require technical support. After the update is complete, verify the new firmware version is installed correctly by checking the system information page.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Scanning
Regular security audits and vulnerability scans are not just good practice; they’re essential for proactive network security. Think of it as a regular health checkup for your network. These audits identify potential weaknesses before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Vulnerability scanners automate the process of identifying known vulnerabilities in your network devices, including your Juniper Session Smart Router. Regular audits by security professionals can provide a more in-depth assessment, identifying potential configuration issues or weaknesses not found by automated scanners. Imagine a scenario where a less obvious misconfiguration allowed attackers access – regular audits can help prevent this. The cost of a proactive approach is significantly less than the cost of a data breach or network compromise.
Securing Juniper Session Smart Routers and Other Network Devices
Beyond firmware updates, implementing robust security measures across your entire network is vital. This involves a multi-layered approach, combining various techniques to create a strong defense. Consider implementing strong password policies – use complex, unique passwords for all devices. Enable features like access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access to sensitive network resources. Regularly review and update your firewall rules. Consider enabling logging and monitoring tools to track network activity and detect suspicious behavior. Keeping your network software up-to-date across all devices is crucial, not just your router. And finally, educate your users about best practices to prevent phishing attacks and other social engineering attempts.
Security Measures to Prevent Future Vulnerabilities
A robust security posture requires a proactive approach. Here’s a list of measures to help prevent similar vulnerabilities in the future:
- Implement a rigorous patch management policy. This includes not only your router but all network devices.
- Utilize a network intrusion detection and prevention system (NIDPS) to monitor network traffic for malicious activity.
- Employ strong authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible.
- Regularly conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to proactively identify and address weaknesses.
- Segment your network to limit the impact of a compromise. This prevents attackers from accessing your entire network if one device is compromised.
- Establish a clear incident response plan to quickly address and contain security incidents.
- Keep detailed logs of all network activity for forensic analysis in case of a security breach.
Illustrative Example
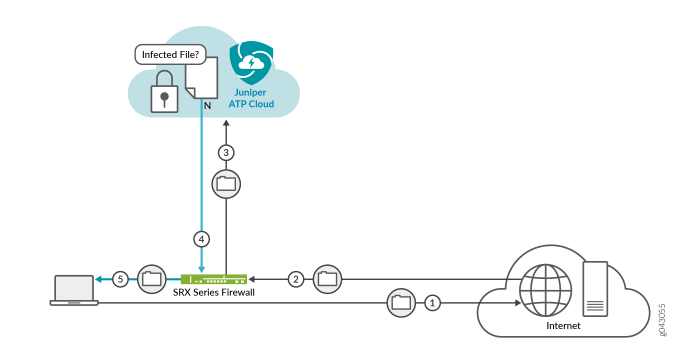
Source: juniper.net
Imagine a scenario where an attacker targets a Juniper Session Smart Router vulnerable to the flaw we’ve discussed. This visual representation details the attack flow, highlighting the attacker’s actions, the exploited vulnerability, and the resulting system compromise. We’ll focus on a specific attack vector, demonstrating how easily the system can be breached.
This example illustrates a successful exploitation of the vulnerability leading to unauthorized access and potential data exfiltration. The attacker leverages a crafted packet to bypass security measures, ultimately gaining control of the router. The visualization will show the sequence of events from the initial reconnaissance to the final compromise.
Attack Flow Diagram
The attack begins with the attacker identifying a vulnerable Juniper Session Smart Router on the network. This is typically done through network scanning to identify devices and versions susceptible to the known vulnerability. Next, the attacker crafts a malicious packet exploiting the specific vulnerability in the router’s session management. This packet, unlike legitimate traffic, contains specific data fields manipulated to trigger the flaw. This manipulated packet is then sent to the targeted router. The router, due to the vulnerability, processes the malicious packet incorrectly, allowing the attacker to bypass authentication and authorization mechanisms. This leads to the creation of an unauthorized administrative session, granting the attacker full control over the router’s configuration and functionalities. The successful exploitation is followed by the attacker establishing a persistent connection to the router, potentially downloading sensitive configuration data or installing malware. The attacker may then use this compromised router as a pivot point to attack other devices on the network.
Network Traffic Analysis, Juniper session smart router flaw
The initial network traffic will show standard port scanning activities from the attacker’s IP address to the target router, attempting to identify open ports and services. Upon discovering the vulnerable service, the attacker initiates a connection using a crafted packet. This malicious packet will appear as legitimate traffic at first glance, but a deeper analysis of the packet headers and payload reveals the malicious intent. Specifically, certain fields within the packet are manipulated to trigger the vulnerability, which will be different depending on the exact nature of the vulnerability. Once the vulnerability is exploited, the network traffic will show the establishment of a new connection from the attacker to the router on administrative ports. This connection will be characterized by the exchange of commands and data, indicating the attacker’s control over the router. The subsequent data transfer could include sensitive information like router configurations, passwords, and network maps, indicating data exfiltration.
Data Flow and System Impact
The data flow begins with the attacker sending the crafted packet. This packet interacts with the vulnerable component within the router’s session management. The flaw in this component allows the attacker’s malicious packet to bypass security checks, leading to the creation of an unauthorized session. The attacker then gains access to the router’s control plane, allowing for arbitrary command execution. This could lead to several impacts, including modification of router configurations, leading to network disruption, denial of service attacks against other network devices, and data exfiltration. The compromised router may be used as a stepping stone to further penetrate the network. The attacker might also install backdoors or malware on the router, maintaining persistent access even after the initial attack. The resulting impact on the system can range from minor configuration changes to complete control, potentially causing significant disruption and data breaches.
Last Word
The Juniper Session Smart Router flaw highlights the ever-present need for vigilance in network security. Regular firmware updates, robust security audits, and a proactive approach to vulnerability management are no longer optional – they’re essential. Failing to address this vulnerability could have catastrophic consequences, so don’t delay. Take action now to secure your network and protect your valuable data. The future of your digital security depends on it.