P2PInfect malware: It sounds like something out of a sci-fi thriller, right? But this isn’t fiction. This insidious malware uses peer-to-peer networks to spread like wildfire, infecting countless devices and wreaking havoc in its wake. We’re diving deep into the dark underbelly of this digital plague, exploring its mechanisms, impact, and how to protect yourself from its clutches. Get ready to unravel the mysteries of P2PInfect and arm yourself with the knowledge to fight back.
From understanding how P2P networks become breeding grounds for this malware to exploring the devastating consequences of an outbreak, we’ll cover everything from prevention strategies and detection techniques to the legal and ethical considerations surrounding this digital menace. Think of this as your ultimate survival guide in the digital Wild West.
Understanding P2P Infect Malware
Source: vietnix.vn
P2P Infect malware represents a sneaky breed of digital threat, leveraging the decentralized nature of peer-to-peer (P2P) networks to spread rapidly and silently. Unlike traditional malware that relies on centralized servers for distribution, P2P Infect malware uses the very structure of P2P networks against us, making it a particularly challenging foe to combat. This makes understanding its mechanics crucial for effective prevention and mitigation.
P2P Infect malware propagation relies on the inherent characteristics of P2P networks: distributed file sharing. Instead of a single source, the malware spreads organically through infected nodes within the network. Each infected machine becomes a potential vector, sharing the malware with other connected peers. This creates a self-replicating, highly resilient system difficult to shut down through simple server takedowns.
P2P Infect Malware Characteristics, P2pinfect malware
P2P Infect malware typically exhibits several key characteristics. It often disguises itself as legitimate software, luring unsuspecting users into downloading and installing it. Once installed, it silently operates in the background, often utilizing encryption and obfuscation techniques to evade detection. The malware’s payload can vary, ranging from data theft and ransomware to botnet participation, enabling malicious actors to perform a wide array of cybercrimes. The decentralized nature of its distribution makes it incredibly difficult to trace back to a single origin point, making attribution and remediation challenging.
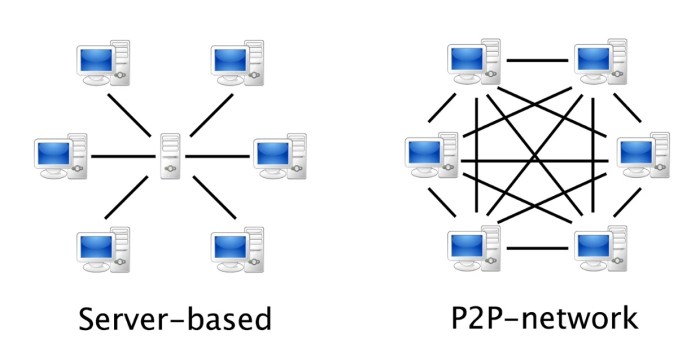
The Role of P2P Networks in Malware Spread
P2P networks, designed for decentralized file sharing, ironically become fertile ground for malware propagation. The anonymity and lack of central control inherent in these networks provide a perfect cover for malicious actors. The sheer volume of shared files makes it difficult to identify and isolate infected ones. Furthermore, the constant exchange of files between peers ensures rapid dissemination, exponentially increasing the malware’s reach. Imagine a wildfire spreading across a vast, interconnected landscape—that’s essentially what P2P Infect malware does within a P2P network.
Comparison with Other Malware Types
Compared to other malware types like viruses or worms, P2P Infect malware stands out due to its reliance on P2P networks for propagation. Viruses typically spread through infected files or email attachments, while worms exploit vulnerabilities to replicate themselves. Unlike these, P2P Infect malware leverages the inherent sharing mechanisms of P2P networks, creating a more resilient and difficult-to-contain threat. Its decentralized nature makes it more resistant to traditional antivirus methods that often rely on signature-based detection.
Exploited Vulnerabilities
P2P Infect malware often exploits several key vulnerabilities. These can include vulnerabilities in P2P software itself, allowing for unauthorized file execution or injection of malicious code. It might also target vulnerabilities in operating systems or applications used by users of the P2P network, leveraging known exploits to gain access and install itself. Weak security practices, such as using default passwords or failing to update software regularly, further exacerbate the risk of infection. For example, a vulnerability in a specific P2P client allowing for remote code execution could be exploited to install the malware on numerous connected devices.
Impact and Consequences of P2P Infect Malware

Source: thestatesman.com
P2P Infect malware, leveraging the decentralized nature of peer-to-peer networks, can wreak havoc on infected systems and networks, causing a ripple effect of damage that extends far beyond the initial point of compromise. Understanding the potential consequences is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies. The impact isn’t just about lost files; it’s about financial losses, reputational damage, and the potential for far-reaching legal repercussions.
Potential Damage Caused by a P2P Infect Malware Outbreak
A P2P Infect malware outbreak can lead to widespread data loss and corruption. Malicious code can delete, encrypt, or modify critical files, rendering systems unusable. Furthermore, the malware can spread rapidly across the network, infecting numerous devices and potentially compromising sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property. The self-replicating nature of P2P Infect malware exacerbates the problem, making containment challenging. System performance can also degrade significantly due to the malware’s resource consumption, leading to slowdowns and crashes.
Financial Implications of a P2P Infect Malware Infection
The financial consequences of a P2P Infect malware infection can be substantial. Direct costs include the expenses associated with remediation, such as hiring cybersecurity experts, restoring data from backups, and replacing damaged hardware. Indirect costs can be even more significant, encompassing lost productivity, business disruption, legal fees, and potential fines for non-compliance with data protection regulations. For example, a ransomware variant delivered through a P2P network could demand a significant ransom for the decryption of critical business data, resulting in substantial financial losses if paid, or even more if the data is irretrievably lost. The cost of recovering from such an attack can easily run into hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of dollars, depending on the size and scope of the infection.
Reputational Risks Associated with a P2P Infect Malware Compromise
A P2P Infect malware compromise can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Data breaches resulting from such infections can lead to loss of customer trust, damage to brand image, and negative media coverage. This reputational damage can have long-term consequences, impacting future business opportunities and investor confidence. Customers may be hesitant to do business with an organization known to have suffered a security breach, leading to a decline in sales and market share. The reputational impact extends beyond the organization itself, potentially affecting partners and affiliates as well.
Examples of Real-World Incidents Involving P2P Infect Malware
While specific details of P2P Infect malware outbreaks are often kept confidential for security reasons, numerous documented cases exist illustrating the devastating consequences. For example, several instances have involved the use of P2P networks to distribute ransomware, where infected computers are used to spread the malware to others. This rapid propagation creates a cascading effect, increasing the difficulty of containment and the overall financial and reputational impact. Additionally, some botnets have leveraged P2P networks for command and control, making them harder to dismantle and leading to large-scale Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. The scale and impact of these incidents highlight the serious threat posed by this type of malware.
Severity of Different P2P Infect Malware Variants
| Malware Variant | Impact | Financial Cost (Estimated) | Reputational Damage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware (e.g., variant distributed via P2P) | Data encryption, system lock-out | $10,000 – $millions (depending on data value and ransom demand) | High – potential for significant negative media coverage and loss of customer trust |
| Botnet component (e.g., part of a DDoS network) | System performance degradation, participation in attacks | Variable – depends on the scale and duration of the attack | Medium – depends on the visibility and impact of the attacks |
| Data Stealer (e.g., stealing credentials via compromised P2P client) | Data theft, identity theft | Variable – depends on the value of stolen data and legal repercussions | High – potential for significant legal action and reputational damage |
| Self-replicating worm | System overload, network disruption | Variable – depends on the scale of infection and the cost of remediation | Medium – depends on the visibility and impact of the network disruption |
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
So, you’ve learned about the nasty realities of P2P Infect malware. Now, let’s flip the script and talk about how to avoid becoming the next victim. Prevention is always better than cure, and with P2P Infect, that’s especially true. A proactive approach is your best defense against this sneaky malware.
Best Practices for Preventing P2P Infect Malware Infections
Implementing strong preventative measures is crucial to avoid infection. This involves a multi-layered approach, combining technical safeguards with user awareness and responsible online behavior. Neglecting any one aspect weakens your overall security posture.
Comprehensive Security Plan to Mitigate Risks
A robust security plan isn’t just about installing antivirus software; it’s about creating a layered defense. Think of it like a castle with multiple walls and defenses – each layer adding extra protection. This plan should include regular software updates, strong passwords, network segmentation, and employee training on safe internet practices. A well-defined incident response plan is also vital; knowing what to do *if* an infection occurs is just as important as preventing it.
Recommended Security Software and Tools
Several tools can help you combat P2P Infect malware. A robust antivirus solution with real-time protection is paramount. Consider software that includes features like behavioral analysis and sandboxing, which can detect and isolate suspicious files before they execute. A firewall, both at the network and application level, is essential for controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. Network monitoring tools can help identify unusual activity that might indicate an infection. Remember, no single tool is a silver bullet; a layered approach is always best.
Importance of Regular Software Updates and Patching
Think of software updates as security patches – they’re like armor upgrades for your digital castle. Software developers constantly release updates to fix vulnerabilities that malware, like P2P Infect, can exploit. Regularly updating your operating system, applications, and antivirus software is not optional; it’s a non-negotiable part of maintaining a secure system. Failing to update leaves gaping holes for malware to infiltrate. Imagine a castle with crumbling walls – easily breached by invaders.
Network Segmentation to Reduce Impact
Network segmentation acts like building separate, fortified sections within your digital castle. By dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments, you limit the impact of a malware infection. If one segment becomes compromised, the malware is less likely to spread to other critical parts of your network. This approach significantly reduces the potential damage and allows for easier containment of the infection. For example, separating your guest Wi-Fi from your internal network limits the damage if a guest device is compromised.
Detection and Response Techniques
P2P Infect malware, sneaky as it is, leaves digital footprints. Detecting and responding effectively requires a multi-pronged approach combining proactive monitoring with swift action upon infection. Understanding the common indicators, implementing robust detection methods, and having a well-defined eradication and recovery plan are crucial for minimizing damage and restoring systems to their pre-infection state.
Effective detection and response hinges on recognizing suspicious activity and implementing a structured approach to containment and recovery. This involves identifying telltale signs of infection, swiftly isolating affected systems, and meticulously eradicating the malware before restoring affected data.
Common Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Identifying IOCs is the first step in detecting a P2P Infect malware infection. These indicators can manifest in various ways, from unusual network activity to performance degradation. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for early detection and prevention of widespread damage.
These indicators often include unusually high network bandwidth consumption, especially during off-peak hours, the appearance of unknown processes consuming significant CPU resources, and the presence of unfamiliar files or directories, particularly in system directories. Furthermore, changes in system settings, such as altered firewall rules or unexpected startup programs, can also point towards a P2P Infect malware infection. Finally, unexpected or unsolicited outgoing network connections to known malicious IP addresses or domains are a strong indicator of compromise.
Detecting a P2P Infect Malware Infection
The detection process involves a combination of proactive monitoring and reactive investigation. Proactive measures include regularly updating antivirus software and employing intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for malicious activity. Reactive measures involve investigating suspicious events, such as performance degradation or unusual network activity, using tools like system monitoring utilities and network analysis tools.
A systematic approach to investigation is key. This starts with analyzing system logs for unusual events, examining running processes for suspicious behavior, and checking for the presence of known malware signatures using updated antivirus software. Network monitoring tools can be invaluable in identifying unusual outbound connections and data transfers. Analyzing system resource utilization can also reveal resource-intensive processes that might be indicative of malware activity. For example, a sudden spike in network upload activity could indicate the malware is actively sharing infected files.
Containing and Eradicating P2P Infect Malware
Containing and eradicating P2P Infect malware requires immediate action to prevent further spread and damage. This typically involves isolating the infected system from the network, terminating malicious processes, and running a full system scan with updated antivirus software. A thorough cleanup of affected files and system settings is also necessary.
Isolation is the first critical step. Disconnect the infected machine from the network to prevent the malware from spreading to other devices. Next, identify and terminate any malicious processes using the Task Manager or a similar tool. This may require administrator privileges. Following this, conduct a thorough system scan with updated antivirus software and remove any identified malware. After the scan, consider running a second scan with a different antivirus engine to ensure complete removal. Finally, review and restore any modified system settings to their original configurations.
Data Recovery Procedures
Data recovery after a P2P Infect malware infection can be challenging, depending on the extent of the damage. If the malware has encrypted files, specialized decryption tools or professional data recovery services might be required. For less severe infections, restoring files from backups is usually the most effective approach.
Before attempting any recovery, ensure the malware is completely eradicated. If backups are available, restoring data from a known clean backup is the safest and most efficient method. If backups are unavailable or corrupted, data recovery software can be employed, but success is not guaranteed and professional assistance may be necessary. Remember to always verify the integrity of recovered data before using it.
Incident Response in a P2P Infect Malware Scenario
Responding to a P2P Infect malware incident requires a structured approach. This involves a series of steps, from initial detection and containment to post-incident analysis and remediation. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of the attack.
The process typically begins with identifying the infected system and isolating it from the network. Next, gather evidence and analyze the extent of the compromise. Then, eradicate the malware and restore affected systems and data. Finally, conduct a post-incident review to identify vulnerabilities and implement preventative measures to avoid future incidents. This systematic approach ensures a swift and effective response, minimizing the damage and preventing future occurrences.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

Source: accurate.id
The creation and distribution of P2P Infect malware carry significant legal and ethical weight, impacting not only the victims but also the creators and those who inadvertently facilitate its spread. Understanding the legal ramifications and ethical responsibilities involved is crucial for both preventing such attacks and responding effectively to them.
The legal landscape surrounding malware is complex and varies across jurisdictions. However, several common legal frameworks apply, often overlapping and intertwining in practice. The severity of penalties depends on factors like the malware’s intent, the scale of the damage inflicted, and the jurisdiction where the crime occurred.
Legal Ramifications of Creating and Distributing P2P Infect Malware
Creating and distributing P2P Infect malware is a serious crime in most countries. Offenders can face prosecution under various laws, including those related to computer fraud and abuse, unauthorized access, data theft, and intellectual property infringement. The specific charges and penalties vary based on the jurisdiction and the severity of the offense. For instance, in the United States, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) provides a legal framework for prosecuting individuals involved in creating and distributing malicious software. Similar legislation exists in many other countries, reflecting a global consensus on the illegality of such activities. Penalties can range from substantial fines to lengthy prison sentences.
Ethical Responsibilities of Cybersecurity Professionals
Cybersecurity professionals bear a significant ethical responsibility in combating P2P Infect malware. This responsibility extends beyond technical expertise to encompass ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, individual rights, and the potential impact of their actions. Ethical guidelines emphasize the importance of acting with integrity, transparency, and a commitment to minimizing harm. This includes adhering to strict professional codes of conduct, respecting legal boundaries, and prioritizing the safety and well-being of users. For example, a cybersecurity professional should not engage in activities that could compromise user privacy or expose sensitive information, even if it involves uncovering malware activity.
Examples of Legal Cases Related to P2P Infect Malware
While specific cases involving “P2P Infect” malware as a named entity are difficult to isolate publicly due to the dynamic and often clandestine nature of malware naming conventions, numerous legal cases exist related to the distribution and impact of peer-to-peer-distributed malware. For example, the prosecution of individuals involved in the creation and distribution of botnets – often spread via P2P networks – frequently results in significant legal consequences. These cases often highlight the challenges of attribution and cross-border investigations, underscoring the complexities of pursuing legal action in the digital realm. The lack of readily available case specifics with “P2P Infect” in the name does not diminish the gravity of the legal consequences associated with similar malware distribution schemes.
Comparison of Legal Frameworks Addressing Malware Distribution
Different legal frameworks exist globally to address malware distribution. Some jurisdictions emphasize strict liability, holding individuals accountable even without intent, while others require demonstrating malicious intent. The legal frameworks also vary in their definitions of “harm,” the types of evidence required for prosecution, and the penalties imposed. International cooperation is crucial for effective prosecution, as malware often transcends national borders. The absence of a single, universally harmonized legal framework necessitates careful consideration of jurisdictional differences when dealing with cross-border malware incidents.
Ethical Guidelines for Handling P2P Infect Malware Incidents
Ethical considerations are paramount when handling P2P Infect malware incidents. A robust ethical framework guides cybersecurity professionals in their actions.
- Prioritize user safety and data protection.
- Maintain transparency and communicate effectively with affected parties.
- Respect legal boundaries and adhere to relevant laws and regulations.
- Refrain from actions that could exacerbate the situation or compromise user privacy.
- Document all actions and decisions meticulously.
- Report incidents to relevant authorities and cooperate fully with investigations.
- Continuously update knowledge and skills to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Future Trends and Challenges: P2pinfect Malware
The landscape of peer-to-peer (P2P) malware is constantly evolving, driven by the ingenuity of malicious actors and the ever-changing technological environment. Understanding these future trends and the challenges they pose is crucial for developing effective countermeasures. The arms race between malware developers and security professionals is ongoing, with each side constantly adapting and innovating.
P2P Infect malware developers are continuously refining their techniques to evade detection and maximize their impact. This includes leveraging advancements in encryption, obfuscation, and polymorphic code generation to make their malware more resilient against traditional antivirus solutions. The use of legitimate P2P networks as conduits for malware distribution also continues to be a significant challenge.
Evolving Tactics of P2P Infect Malware Developers
Malware developers are increasingly employing sophisticated techniques to bypass security measures. These include using advanced encryption algorithms to conceal malicious code, employing polymorphic techniques to change the malware’s signature frequently, and leveraging legitimate software vulnerabilities for easier infiltration. The use of botnets, coordinated networks of infected computers, significantly amplifies the malware’s reach and destructive potential. For instance, the Mirai botnet, while not strictly P2P, demonstrated the devastating impact of large-scale coordinated attacks leveraging compromised IoT devices, highlighting the potential for similar tactics within the P2P ecosystem.
Emerging Threats Related to P2P Infect Malware
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents a significant new vulnerability. The sheer number of interconnected devices, many lacking robust security measures, provides a vast pool of potential targets for P2P malware. Furthermore, the increasing use of cloud storage and services creates new opportunities for malware to spread rapidly and exploit data. The integration of AI and machine learning in malware development is also a concerning trend, potentially leading to more adaptive and difficult-to-detect threats. Imagine a self-learning P2P malware that autonomously adapts its infection strategy based on the security measures it encounters.
Challenges in Combating P2P Infect Malware
Combating P2P Infect malware presents several significant challenges. The decentralized nature of P2P networks makes tracking and eliminating infected nodes extremely difficult. The constant evolution of malware tactics requires continuous adaptation of security solutions. Furthermore, the global nature of the internet makes it challenging to coordinate international efforts to combat the spread of P2P malware. Resource limitations, both in terms of funding and skilled personnel, further hinder effective response strategies.
Potential Future Developments in P2P Infect Malware Technology
Future P2P malware could leverage advanced AI techniques for self-propagation and adaptation. This could involve machine learning algorithms that analyze network traffic and system defenses to optimize infection strategies and evade detection. We could also see a rise in sophisticated polymorphic malware that constantly changes its code, making it extremely difficult to identify and neutralize. The convergence of P2P malware with other attack vectors, such as phishing or social engineering, could also lead to more effective and widespread infections.
Artificial Intelligence for Detection and Prevention
Artificial intelligence offers promising avenues for improving the detection and prevention of P2P Infect malware. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify patterns and anomalies in network traffic and system behavior that indicate the presence of malware. AI-powered sandboxing techniques can analyze the behavior of suspicious files in a controlled environment, allowing for more accurate identification of malicious code without risking infection of the actual system. Furthermore, AI can assist in the development of more adaptive and robust security solutions capable of countering the evolving tactics of malware developers. Real-time threat intelligence, powered by AI, can help anticipate and mitigate emerging threats before they become widespread.
Final Summary
P2PInfect malware isn’t just a tech problem; it’s a societal one. Its ability to spread rapidly and cause widespread damage highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity practices. While the fight against this digital threat is ongoing, understanding its workings, implementing preventative measures, and staying informed about the latest developments are crucial steps in safeguarding ourselves and our digital world. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay safe.