Netgear routers bypass authentication: It sounds like a sci-fi thriller, right? But unfortunately, it’s a very real threat. Hackers are constantly looking for weaknesses in our home and business networks, and Netgear routers, like any other device, are vulnerable. This isn’t about fear-mongering; it’s about understanding how these vulnerabilities arise – from outdated firmware and default passwords to more complex exploits – and how to protect yourself. We’ll dissect the common attack methods, explore the consequences of a successful breach, and, most importantly, equip you with the knowledge to secure your Netgear router and keep your data safe.
We’ll cover everything from understanding common vulnerabilities and the importance of firmware updates to implementing strong password practices and leveraging network security best practices. Think of this as your ultimate guide to fortifying your Netgear router against unauthorized access – because a compromised network is a headache you definitely want to avoid.
Security Vulnerabilities in Netgear Routers
Netgear routers, while popular for their ease of use and affordability, have unfortunately been the target of numerous security vulnerabilities over the years. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, can compromise the security of your home network, leaving your personal data and connected devices at risk. Understanding these vulnerabilities and how attackers exploit them is crucial for maintaining a secure home network.
Common Vulnerabilities Allowing Authentication Bypass
Several vulnerabilities can allow attackers to bypass authentication on Netgear routers, granting them unauthorized access to the router’s administrative interface. These vulnerabilities often stem from weaknesses in the router’s firmware, poorly implemented security features, or default credentials that are easily guessable. Successful exploitation can provide complete control over the network, enabling attackers to monitor traffic, redirect users to malicious websites, install malware, and even use the router as a launchpad for further attacks.
Attacker Exploitation Methods
Attackers utilize various methods to exploit these vulnerabilities. Common techniques include brute-force attacks, where they try numerous password combinations until they find the correct one, and SQL injection, where they inject malicious SQL code into the router’s login form to gain access. Exploiting known vulnerabilities in the router’s firmware, often through the use of readily available exploits, is another common approach. Some attackers might even leverage vulnerabilities in the router’s web interface to execute arbitrary commands, effectively taking over the device. Furthermore, phishing attacks can trick users into revealing their router credentials, providing attackers with easy access.
Examples of Vulnerable Netgear Router Models and Associated CVEs
Numerous Netgear router models have been affected by authentication bypass vulnerabilities over time. While specific vulnerabilities and their associated CVEs change frequently as new weaknesses are discovered and patched, it’s crucial to keep your router’s firmware updated. For instance, some older models, like the Netgear Nighthawk R7000, have been affected by vulnerabilities (specific CVEs would need to be researched from reputable sources like the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) at the time of writing, as they change frequently) that allowed attackers to gain unauthorized access by exploiting weaknesses in the web interface. Similarly, various other Netgear models have faced similar issues, highlighting the ongoing need for robust security practices and timely firmware updates.
Vulnerability Summary Table
| Vulnerability Type | Affected Models (Examples – Consult NVD for comprehensive list) | Exploitation Method | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Various Netgear models (check NVD for specific models and CVEs) | Injecting malicious JavaScript code into the router’s web interface. | Regular firmware updates, input validation, and secure coding practices. |
| Command Injection | Various Netgear models (check NVD for specific models and CVEs) | Injecting malicious commands into the router’s input fields. | Input sanitization, parameterized queries, and secure coding practices. |
| Default Credentials | Various Netgear models (check NVD for specific models and CVEs) | Using default or easily guessable passwords. | Changing default passwords to strong, unique passwords immediately after installation. |
| Weak Authentication Mechanisms | Various Netgear models (check NVD for specific models and CVEs) | Exploiting weaknesses in the router’s authentication protocols. | Enabling strong authentication protocols (where available), such as WPA2/WPA3. |
Firmware Updates and Their Role in Security
Source: 19216811.uno
Keeping your Netgear router’s firmware up-to-date is crucial for maintaining its security. Outdated firmware is like leaving your front door unlocked – it’s an open invitation for hackers to exploit known vulnerabilities. Regular updates patch these security holes, preventing malicious actors from gaining unauthorized access to your network and potentially compromising your sensitive data.
Outdated firmware significantly contributes to authentication bypass vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to circumvent the normal login process, granting them complete control over your router without needing a password. This control can be used for various nefarious purposes, from stealing your internet bandwidth to launching attacks against other devices on your network. The longer you delay updating, the greater the risk becomes.
Security Patches Addressing Authentication Flaws
Netgear regularly releases firmware updates that address specific security flaws, including authentication bypass vulnerabilities. For instance, several firmware versions in the past contained vulnerabilities that allowed attackers to exploit weaknesses in the router’s authentication mechanisms, potentially allowing for remote code execution. These vulnerabilities were subsequently patched in later firmware releases. While specific CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) numbers are dynamic and constantly changing, Netgear’s release notes often detail the specific security enhancements included in each update. These notes should always be reviewed carefully to understand the scope of improvements. For example, a release might explicitly state that it addresses a vulnerability that allowed an attacker to bypass the router’s password authentication system via a specific network request.
Updating Netgear Router Firmware: A Step-by-Step Guide
Regularly checking for and installing firmware updates is a simple yet powerful security measure. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure your Netgear router is always running the latest, most secure firmware:
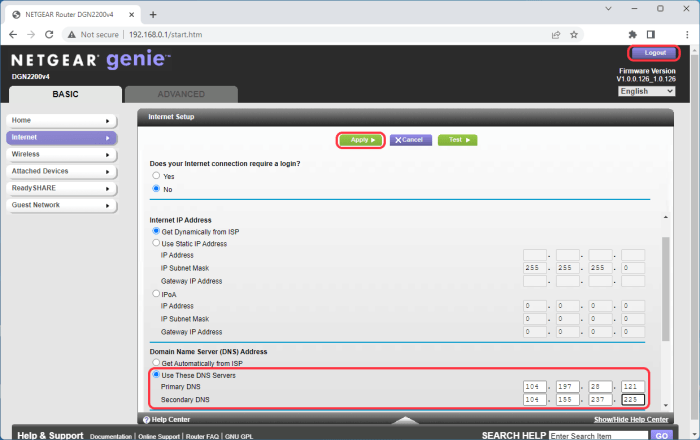
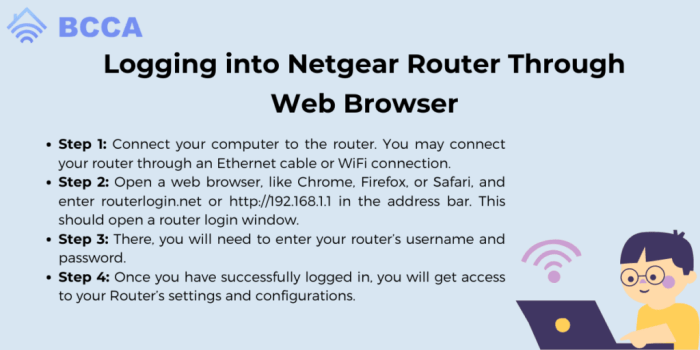
- Access your router’s administration interface: Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1) into the address bar. You’ll need your router’s username and password to log in.
- Locate the firmware update section: The exact location varies depending on your router model, but generally, you’ll find a section labeled “Firmware Update,” “System,” “Administration,” or something similar in the router’s settings menu.
- Check for updates: Look for a button or option to check for new firmware. The router will connect to Netgear’s servers to see if a newer version is available.
- Download and install the update: If an update is found, download it and follow the on-screen instructions to install it. This process usually involves uploading the firmware file to the router. Important: During the update process, do not interrupt the power supply to the router.
- Reboot your router: Once the update is complete, the router will likely reboot automatically. If not, reboot it manually to ensure the new firmware is fully loaded.
- Verify the update: After the reboot, log back into the router’s administration interface and check the firmware version to confirm that the update was successfully installed.
Default Passwords and Their Implications
Source: safesurfer.io
Leaving your Netgear router with its factory-default password is like leaving your front door unlocked – a wide-open invitation for trouble. It’s a security vulnerability that can easily be exploited by malicious actors, potentially leading to significant consequences for your network and personal data. Understanding the risks associated with default passwords is crucial for protecting your home network.
Default passwords are pre-programmed login credentials set by the manufacturer. While convenient for initial setup, they pose a significant security risk because they are publicly available and easily discoverable through simple online searches. Attackers leverage this readily available information to gain unauthorized access to your router, effectively controlling your entire network. This gives them the power to steal sensitive information, install malware, launch attacks against other devices, or even use your internet connection for illicit activities. The consequences can range from minor inconveniences to major financial and privacy breaches.
Risks Associated with Using Default Passwords
Using default passwords on your Netgear router exposes your network to a range of serious threats. Attackers can easily find these passwords online, allowing them to access your router’s administration panel. Once inside, they can modify your router’s settings, reroute your internet traffic, install malicious software, and even use your network for illegal activities. The risk is amplified if you use your router for sensitive tasks like online banking or accessing personal accounts. Furthermore, a compromised router can become a launching pad for attacks against other devices on your network, compromising your entire digital ecosystem. The potential for damage is significant and far-reaching.
Methods of Exploiting Default Passwords, Netgear routers bypass authentication
Attackers employ various techniques to exploit default passwords. The simplest method involves a brute-force attack, systematically trying common passwords until they find the correct one. This is particularly effective with default passwords, which are often short, predictable, and widely known. Another method is using readily available online databases containing lists of default passwords for various router models. These databases are easily accessible, providing attackers with a pre-compiled list of potential passwords to try. Sophisticated attackers may also use automated tools that scan for vulnerable routers and automatically attempt to log in using common default passwords. The speed and efficiency of these tools increase the likelihood of a successful breach.
Examples of Common Default Passwords
While Netgear actively discourages the use of default passwords, examples of commonly found default passwords (though not necessarily currently used by Netgear) include “password,” “admin,” “1234,” and variations of these. It’s crucial to remember that these are just examples; the specific default password varies depending on the Netgear router model and firmware version. However, the principle remains the same: default passwords are inherently insecure and should never be used in a production environment. It is imperative to change the default password immediately after setting up your router.
Changing the Default Password on a Netgear Router
Changing your Netgear router’s password is a straightforward process, but critical for security. Here’s how to do it:
- Access your router’s administration panel by typing its IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser’s address bar.
- Log in using the default username and password (often “admin” for both).
- Navigate to the “Administration” or “Security” section of the router’s settings.
- Locate the “Password” or “Wireless Password” option.
- Enter your desired new password, ensuring it’s strong, unique, and difficult to guess. A strong password typically includes a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Save the changes. Your router will likely reboot to apply the new settings.
Remember, a strong and unique password is your first line of defense against unauthorized access. Regularly updating your router’s firmware is also crucial to patching known vulnerabilities and maintaining optimal security.
Network Security Best Practices for Netgear Routers
Source: bcca.org
So, you’ve got a Netgear router – awesome! But a powerful router needs equally strong security to prevent unwelcome guests from crashing your digital party. This isn’t about paranoia; it’s about proactive protection. Let’s dive into the best practices to keep your network safe and sound. We’ll cover password management, firmware updates, network segmentation, and access control, ensuring your Netgear router acts as a robust digital fortress, not a flimsy gate.
Password Management
Strong passwords are the foundation of any secure network. Weak passwords are like leaving your front door unlocked – an open invitation for trouble. Here’s how to fortify your Netgear router’s defenses:
- Use a unique, complex password for your router’s administration interface. Think long (at least 12 characters), varied (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols), and unpredictable. Avoid using personal information or easily guessable words.
- Change the default administrator password immediately after setting up your router. Default passwords are widely known and easily accessible to malicious actors.
- Regularly update your router’s admin password, ideally every few months. This reduces the risk of compromise over time.
- Enable password complexity requirements within the router’s settings to enforce strong password creation for all users.
Firmware Updates
Your router’s firmware is its operating system. Just like your phone or computer, it needs regular updates to patch security vulnerabilities. Neglecting updates leaves your network vulnerable to exploitation.
- Check for firmware updates regularly through the Netgear website or your router’s interface. Netgear often releases updates to address security flaws.
- Install updates promptly. Don’t delay – the longer you wait, the greater the risk of compromise.
- Back up your router’s configuration before installing major firmware updates. This allows for easy restoration in case of unforeseen issues.
Network Segmentation
Think of your network as a house. You wouldn’t want strangers wandering freely through every room. Network segmentation creates separate “rooms” on your network, limiting the impact of a breach.
- Use a guest network to isolate visitors’ devices from your main network. This prevents unauthorized access to your personal data and devices.
- Consider using VLANs (Virtual LANs) to further segment your network, separating sensitive devices like servers or IoT devices from less critical devices.
- Implement access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access to specific network resources based on IP addresses or device types.
Access Control
Access control limits who can access your network and what they can do once they’re in. It’s about creating a controlled environment.
- Enable MAC address filtering to restrict access to only authorized devices. This adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Disable remote administration access unless absolutely necessary. This prevents unauthorized access from outside your local network.
- Regularly review and update your access control rules to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Enabling WPA2/3 Encryption and Firewall Protection
These are fundamental security features that should always be enabled.
- WPA2/3 Encryption: WPA2/3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) encrypts your wireless network traffic, making it much harder for unauthorized users to intercept your data. Ensure your Netgear router is configured to use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption, the strongest available options.
- Firewall Protection: A firewall acts as a gatekeeper, blocking unauthorized access attempts to your network. Enable the built-in firewall on your Netgear router and configure it appropriately to protect against external threats. Consider configuring firewall rules to block specific ports or IP addresses.
Secure Network Configuration Illustration
Imagine this: Your Netgear router sits at the center. Connected to it are two separate networks: a main network for your personal devices (computers, smartphones, etc.), secured with WPA3 encryption and protected by a firewall, and a guest network, also secured with WPA2 encryption but separated from the main network, preventing guests from accessing personal data. Each network has its own access controls, limiting access based on MAC addresses or IP addresses. Regular firmware updates keep everything patched and up-to-date. This visual represents a layered approach to security, adding multiple levels of protection.
Consequences of Authentication Bypass
A successful authentication bypass on a Netgear router opens a Pandora’s Box of potential problems, ranging from minor inconveniences to catastrophic data loss and financial ruin. The severity of the consequences depends heavily on the type of network compromised – a home network versus a business network – and the attacker’s goals. Understanding these potential repercussions is crucial for implementing robust security measures.
The impact of a compromised Netgear router extends far beyond a simple inconvenience. It represents a significant vulnerability that can expose sensitive personal and financial information, disrupt operations, and even facilitate more extensive cyberattacks.
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
An authentication bypass grants an attacker complete control over the router, effectively making them the network administrator. This allows them to intercept all network traffic, including passwords, credit card details, emails, and other sensitive data transmitted over unencrypted connections. Furthermore, they can access and modify router settings, potentially redirecting internet traffic to malicious websites or installing malware. Imagine a scenario where a hacker gains access to your home network through a compromised router. They could potentially steal your banking credentials, access your personal photos, or even monitor your online activity. In a business setting, the consequences are amplified; confidential client data, proprietary information, and financial records become vulnerable, potentially leading to significant legal and financial repercussions.
Network Manipulation and Denial of Service
Beyond data theft, an attacker can manipulate the network in various ways. They could launch denial-of-service (DoS) attacks against other devices on the network, rendering them inaccessible. They could also install malware on connected devices or use the router as a launching point for further attacks on other networks. Consider a small business reliant on its network for operations. A successful authentication bypass could cripple their entire system, leading to lost productivity, financial losses due to downtime, and potential damage to their reputation. This disruption could range from minor inconveniences to complete business paralysis, depending on the attacker’s actions and the business’s reliance on the network.
Real-World Examples of Authentication Bypass Exploitation
While specific details of many attacks remain confidential for security reasons, publicly available information illustrates the potential damage. News reports have documented instances where vulnerabilities in routers, including some Netgear models, were exploited to launch large-scale botnet attacks. These botnets, comprised of compromised devices, are then used for various malicious activities, including spamming, distributed denial-of-service attacks, and cryptocurrency mining. In other cases, compromised routers have been used to steal personal information from unsuspecting users, leading to identity theft and financial fraud. The Mirai botnet, for example, leveraged vulnerabilities in numerous IoT devices, including routers, to launch massive DDoS attacks, highlighting the far-reaching consequences of insecure devices. These real-world examples demonstrate the critical need for robust security measures to prevent authentication bypass.
Mitigation Techniques and Tools: Netgear Routers Bypass Authentication
Protecting your Netgear router from authentication bypass vulnerabilities requires a multi-layered approach. Ignoring these vulnerabilities leaves your network wide open to malicious actors, potentially leading to data breaches, unauthorized access, and significant financial losses. Implementing robust mitigation strategies and utilizing effective security tools are crucial for safeguarding your network.
Strengthening Router Security
A strong defense begins with fundamental security practices. Regularly updating your router’s firmware is paramount; these updates often include patches for known vulnerabilities, including those that could lead to authentication bypass. Choosing a strong, unique password—one that’s long, complex, and not easily guessable—is also vital. Avoid default passwords at all costs. Enabling features like WPA3 encryption enhances the security of your Wi-Fi network, making it harder for attackers to intercept your data. Furthermore, regularly reviewing your router’s access control lists (ACLs) to ensure only authorized devices can connect is a crucial step in mitigating risk.
Security Tools for Router Protection
Several security tools can help detect and prevent authentication bypass attempts. These tools offer varying levels of protection and functionality, and the best choice depends on your specific needs and technical expertise. Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, alerting you to potential attacks. Network-based firewalls filter traffic based on pre-defined rules, blocking malicious connections before they reach your router. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, including your router, to identify potential threats and security incidents. Finally, vulnerability scanners actively scan your router for known weaknesses, providing insights into potential security gaps.
Comparison of Security Tools
Choosing the right security tool requires careful consideration of its features, strengths, and weaknesses. The following table compares some popular options:
| Tool Name | Functionality | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snort (IDS/IPS) | Network intrusion detection and prevention | Open-source, highly customizable, large community support, effective at detecting known attacks | Requires technical expertise to configure and manage, can generate a high volume of false positives |
| pfSense (Firewall) | Network firewall with advanced features like VPN and IDS/IPS | Open-source, highly configurable, robust security features, good performance | Steeper learning curve than some commercial firewalls, requires technical expertise |
| AlienVault OSSIM (SIEM) | Security information and event management | Open-source, collects and analyzes logs from multiple sources, provides centralized security monitoring | Can be complex to set up and manage, requires significant resources |
| Nessus (Vulnerability Scanner) | Vulnerability scanning and assessment | Comprehensive vulnerability database, automated scanning, detailed reporting | Can be expensive, requires technical expertise to interpret results, may generate false positives |
Conclusive Thoughts
Securing your Netgear router against authentication bypass isn’t about being a cybersecurity expert; it’s about taking proactive steps to protect your valuable data and online privacy. By understanding the vulnerabilities, staying updated with firmware patches, and adopting robust security practices, you significantly reduce the risk of a potentially devastating breach. Remember, a little vigilance goes a long way in maintaining a secure digital environment. So, take control of your network security and keep those hackers at bay!